New Features in CDH 6.2.0
See below for new features in CDH 6.2.0, grouped by component:
Apache Accumulo
There are no notable new features in this release.
Apache Avro
There are no notable new features in this release.
Apache Crunch
There are no notable new features in this release.
Apache Flume
-
Flume HDFS Sink retries close a configurable number of times with a configurable interval in between before attempting the recoverLease.
-
Global SSL keystore parameters can be specified through the standard -D JSSE system properties or in environment variables. Component-level configuration is also possible.
-
Update to Kafka 2.0 client.
-
SSL/TLS support for syslog and multi port syslog sources has been added.
-
The new default of hdfs.callTimeout is 30 sec.
-
Two new interfaces for getting the transaction capacity and the batch size fields have been added to prevent source batch size larger than the channel transaction capacity.
For more information on new features and improvements added in Flume 1.9, see the Apache Flume 1.9 Release Notes.
Apache Hadoop
Hadoop Common
There are no notable new features in this release.
HDFS
The following are some of the new features in this release of HDFS:
JournalNode Synchronization
CDH now supports synchronizing the contents of JournalNodes in the cluster. This capability helps in maintaining consistency in the contents of all the JournalNodes across the cluster.
For more information, see Synchronizing the contents of JournalNodes.
Option for fixing misreplicated blocks
The hdfs fsck command now includes the -replicate option which triggers the replication of misreplicated data blocks.
For more information, see Fixing Block Inconsistencies.
MapReduce
There are no notable new features in this release.
YARN
The following are some of the notable new features in this release of YARN:
GPU Usage
CDH supports NVIDIA GPU as a resource for YARN. GPU use can be enabled with Cloudera Manager.
For more information, see Enable GPU Using Cloudera Manager.
Custom Resource Types
CDH supports the definition and management of custom resources. This means that the resource system in YARN is configurable. Resources can be created with Cloudera Manager.
For more information, see Create Custom Resource Using Cloudera Manager.
Apache HBase
The following are some of the notable new features in this release of HBase:
HBase Pre-Upgrade Tools Checkbox
There are three pre-upgrade tools that help you to validate HBase compatibility when upgrading a CDH 5 cluster to CDH 6:
- hbase pre-upgrade validate-dbe and hbase pre-upgrade validate-hfile: These tools validate that none of your tables or snapshots uses the PREFIX_TREE Data Block Encoding.
- hbase pre-upgrade validate-cp: This tool validates that your co-processors are compatible with the upgrade.
When you are attempting to upgrade from a CDH 5 cluster to a CDH 6 cluster checkboxes appear to ensure that you have performed all the HBase related pre-upgrade migration steps. For more information, see Migrating Apache HBase Before Upgrading to CDH 6.
HBase Serial Replication
- Specify the SERIAL => true flag when a new peer is created:
hbase> add_peer 'serialpeer1', CLUSTER_KEY => "cluster.example.com:2181:/hbase", SERIAL => true
- Modify an existing peer:
hbase> set_peer_serial ''serialpeer1', true
If Lily HBase NRT Indexer Service is used, Cloudera recommends not to use HBase Serial Replication as it causes additional delays to propagate updates to Solr.
Additional IO Engine Support
- mmap: Stores and accesses cache through memory mapping to a file under a specified path.
- pmem: Uses the direct access capabilities from a persistent memory devices. It can be configured only for paths mounted on DC PMEM devices.
These two engines can be configured only in Cloudera Manager using safety valve. For more information, see Configuring the Off-heap BucketCache.
Apache Hive / Hive on Spark / HCatalog
Continue reading:
Apache Hive
The following are some of the notable new features in this release of Hive:
Compile Lock Removal
Hive now supports the removal of the query compilation lock. Deactivating the compilation lock enables a controlled number of queries to compile in parallel. The default degree of parallelism (number of workers) is three, and users can configure this in Cloudera Manager depending on their needs.
Learn more about this feature in Removing the Hive Compilation Lock.
Dynamic Partition Insert
You can now issue a query to add partitions to HMS in batch instead of 1-by-1. If you insert a large number, such as 1-2k, of partitions you can experience timeout issues. Adjust hive.metastore.client.socket.timeout (when using Hive) and spark.hadoop.hive.metastore.client.socket.timeout (when using Spark). Try a value of 600 seconds of timeout to alleviate the problem.
Secured S3 Credentials for Hive
S3 credentials are now stored securely by Cloudera Manager for use with Hive. This enables multi-user Hive-on-S3 clusters.
Learn more at Configuring the Amazon S3 Connector.
Secured ADLS Credentials for Hive
ADLS credentials are now stored securely via Cloudera Manager for use with Hive. This enables multi-user Hive-with-ADLS clusters.
Learn more at Configuring ADLS Access Using Cloudera Manager.
Hive on Spark
There are no notable new features in this release.
Hue
The following are some of the notable new features in this release of Hue.
Apache Tez Integration Improvements
Now when you are using Tez as the query execution engine for Hive, jobs are displayed in the Hue Job Browser. The query ID is printed and query progress is displayed.
For more information about this improvement, see the Hue blog.
Enhanced Impala SQL Query Troubleshooting
Graphical displays of Impala SQL query profiles have been enhanced with greater detail. This added information helps you understand where and why query bottlenecks occur and how to optimize your queries to eliminate them. For example, detailed information is now provided about CPU processing time and network or disk I/O time for each node of query execution:
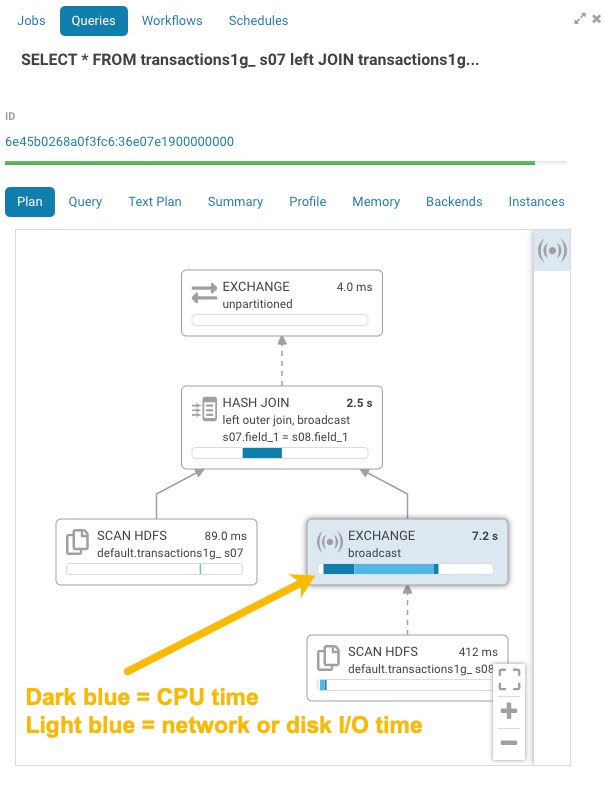
In addition, click the header of the pane to open a details panel:
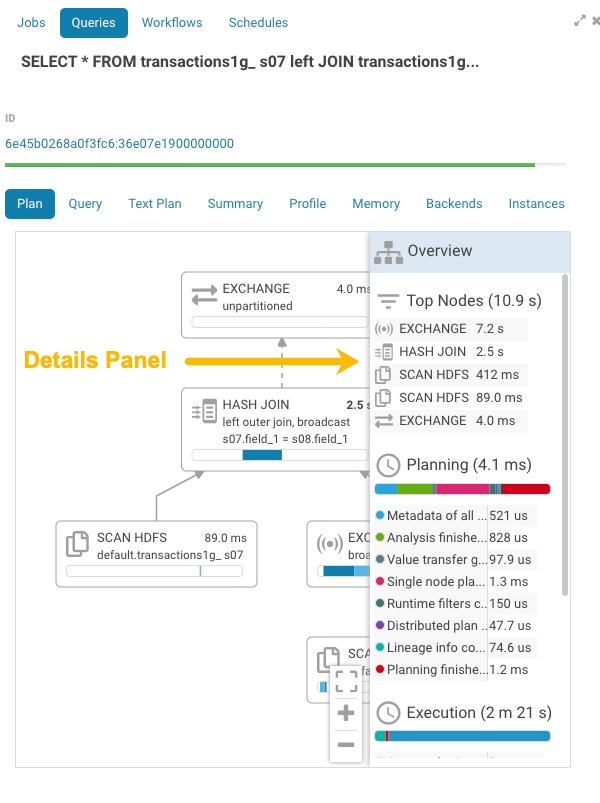
To access this feature:
- Run a query in the Hue Impala editor.
- From the menu on the left, launch the Job Browser.
- In the Job Browser, select the Queries tab.
- In the list of queries, click on the query that you just ran to launch the graphical display of the query.
For more information about this new feature, see the Hue blog.
Apache Impala
The following are some of the notable new features in this release of Impala.
Multi-cluster Support
- Remote File Handle Cache
Impala can now cache remote HDFS file handles when the ‑‑cache_remote_file_handles impalad flag is set to true. This feature does not apply to non-HDFS tables, such as Kudu or HBase tables, and does not apply to the tables that store their data on cloud services such as S3 or ADLS.
See Scalability Considerations for File Handle Caching for file handle caching in Impala.
Enhancements in Resource Management and Admission Control
- Admission Debug page is available in Impala Daemon web UI at
/admission and provides the following information about Impala resource pools.
- Pool configuration
- Relevant pool stats
- Queued queries in order of being queued (local to the coordinator)
- Running queries (local to this coordinator)
- Histogram of the distribution of peak memory usage by admitted queries
- A new query option, NUM_ROWS_PRODUCED_LIMIT, was added to limit the number of rows returned from queries.
Impala will cancel a query if the query produces more rows than the limit specified by this query option. The limit applies only when the results are returned to a client, e.g. for a SELECT query, but not an INSERT query. This query option is a guardrail against users accidentally submitting queries that return a large number of rows.
Metadata Performance Improvements
- Automatic Metadata Sync using Hive
Metastore Notification Events
When enabled, the catalogd polls Hive Metastore (HMS) notifications events at a configurable interval and syncs with HMS. You can use the new web UI pages of the catalogd to check the state of the automatic invalidate event processor.
Note: This is a preview feature in CDH 6.2, and you should not use the feature without the guidance of Cloudera Support. If you are interested in using the feature, file a support ticket and work through Cloudera Support.
Compatibility and Usability Enhancements
- Impala can now read the TIMESTAMP_MILLIS and TIMESTAMP_MICROS Parquet types.
See Using the Parquet File Format with Impala Tables for the Parquet support in Impala.
- The LEVENSHTEIN string function is supported.
The function returns the Levenshtein distance between two input strings, the minimum number of single-character edits required to transform one string to another.
- The IF NOT EXISTS clause is supported in the ALTER TABLE statement.
- Extended or verbose EXPLAIN
output includes the following new information for queries:
- The text of the analyzed query that may have been rewritten to include various optimizations and implicit casts.
- The implicit casts and literals shown with the actual types.
- CPU resource utilization (user, system, iowait) metrics were added to the Impala profile outputs.
Security Enhancement
The REFRESH AUTHORIZATION statement was implemented for refreshing authorization data.
Apache Kafka
The following are some of the notable new features in this release of Kafka CDH 6.2.0.
Rebase on Apache Kafka 2.1.0
The Kafka version in CDH 6.2.0 is based on Apache Kafka 2.1.0.
-
The internal schema used to store consumer offsets has been changed.
-
Support for Zstandard compression has been added.
-
Unclean leader election is automatically enabled by the controller when unclean.leader.election.enable config is dynamically updated by using per-topic config override.
-
A new method AdminClient#metrics(), has been added to AdminClient. This allows any application using the AdminClient to gain more information and insight by viewing the metrics captured from the AdminClient.
New Metrics
A number of new metrics are introduced for Kafka. The following list is only a summary, for full list of metrics, see Metrics Reference.
-
Zookeeper Request Latency
-
Consumer Groups Completing Rebalance
-
Consumer Groups Dead
-
Consumer Groups Empty
-
Consumer Groups Preparing Rebalance
-
Consumer Groups Stable
-
Zookeeper Auth Failures
-
Zookeeper Disconnects
-
Zookeeper Expires
-
Zookeeper Read Only Connects
-
Zookeeper Sasl Authentications
-
Zookeeper Sync Connects
-
Incremental Fetch Session Evictions Rate
-
Number of Incremental Fetch Partitions Cached
-
Number of Incremental Fetch Sessions
-
Unclean Leader Election Enable Rate and Time
Support for Authentication with Delegation Tokens
As of CDH 6.2.0, Cloudera supports delegation token based authentication on Kafka clusters. Delegation token based authentication is a lightweight authentication method designed to complement existing SASL authentication. Although Kafka delegation tokens make use of the SCRAM authentication model, SCRAM is not supported. For more information, see Kafka Delegation Tokens.
Broker IDs are visible on the instance page in Cloudera Manager
Broker IDs can now be easily viewed in Cloudera Manager. To view broker IDs select the Kafka service and go to Instances. The broker IDs can be found next to each Kafka broker instance enclosed in brackets.
Default Behaviour Changes
- Unclean leader election is automatically enabled by the controller when unclean.leader.election.enable config is dynamically updated by using per-topic config override.
-
Diagnostic data bundles collected by Cloudera Manager from now on include information on Kafka topics. The bundle includes the information exposed by the following two commands:
-
kafka-topics --describe
-
kafka-topics --list
-
Apache Kudu
The following are some of the notable new features and enhancements in this release of Kudu:
-
Kudu now supports location awareness. The rack assignments made in Cloudera Manager will be used in Kudu automatically.
The kudu cluster rebalance tool has been updated to act in accordance with the placement policy of a location-aware Kudu.
Upon upgrading, if rack locations are assigned, you should run the kudu cluster rebalance tool to ensure your existing tables are in compliance with the rack awareness placement policy.
See Kudu Administration for more information about this feature.
-
When creating a table, the master now enforces a restriction on the total number of replicas rather than the total number of partitions. If manually overriding --max_create_tablets_per_ts, the maximum size of a new table has effectively been cut by a factor of its replication factor. Note that partitions can still be added after table creation.
-
The compaction policy has been updated to favor reducing the number of rowsets. This can lead to faster scans and lower bootup times, particularly in the face of a “trickling inserts” workload, where rows are inserted slowly in primary key order.
-
Anew tablet-level metric, average_diskrowset_height, shows how much a replica needs to be compacted, as indicated by the average number of rowsets per unit of keyspace.
-
Scans which read multiple columns of tables undergoing a heavy UPDATE workload are now more CPU efficient. In some cases, scan performance of such tables may be several times faster upon upgrading to this release.
-
Kudu-Spark users can now provide the short “kudu” format alias to Spark. This enables using .format(“kudu”) in places where you would have needed to provide the fully qualified name like .format(“org.apache.kudu.spark.kudu") or imported org.apache.kudu.spark.kudu._ and used the implicit .kudu functions. See Kudu Integtraion with Spark for detail.
-
The KuduSink class has been added to the Spark integration as a StreamSinkProvider, allowing structured streaming writes into Kudu.
-
The amount of server-side logging has been greatly reduced for Kudu’s consensus implementation and background processes. This logging was determined to be not useful and unnecessarily verbose.
-
The Kudu web UI now clearly indicates which columns are a part of the primary keys.
-
The new kudu table describe tool describes table attributes, including schema, partitioning, replication factor, column encodings, compressions, and default values.
-
The new kudu table scan tool scans rows from a table, supporting comparison, in-list, and is-null predicates.
-
The new kudu locate_row tool allows users to determine what tablet a given primary key belongs to, and whether a row exists for that primary key.
-
The new kudu diagnose dump_mem_trackers tool allows users to output the contents of the /mem‑trackers web UI page in the CSV format.
Apache Oozie
There are no notable new features in this release.
Apache Parquet
The following are some of the notable new features in this release of Parquet:
Support for New Logical Type Representation
A new, more flexible logical type API has been introduced in parquet-mr—based on the Thrift field in parquet-format, which has been available for a while. The new API allows storage and retrieval of different type attributes, for example, timestamp semantics and precision.
The new logical types are represented by the LogicalTypeAnnotation class and are entirely forward- and backward-compatible with the previous logical types. Files written using the old API can be read using the new API, and as long as no new types are used, files written using the new API can also be read using the old API.
Apache Phoenix
Starting with Apache Phoenix 5.0.0/ CDH 6.2.0, Phoenix parcel can be installed and used with CDH. You can download and install the Phoenix parcel on CDH 6.2.0. For more information about installing and using Phoenix, see the Phoenix Guide.
Apache Pig
There are no notable new features in this release.
Cloudera Search
There are no notable new features in this release.
Apache Sentry
There are no notable new features in this release.
Apache Spark
Spark Driver Logs
The Spark service collects Spark driver logs when Spark applications are run in YARN-client mode or with the Spark Shell. This feature is enabled by default, and the logs are persisted to an HDFS directory and included in YARN Diagnostic Bundles.
To disable this feature, uncheck Persist Driver Logs to Dfs on the Configuration page of your Spark service.
For more information, see Collecting Spark Driver Logs.
Spark Structured Streaming reference application for CDH
The Spark structured streaming reference application is a project that includes sample applications that demonstrate an Apache Kafka -> Apache Spark Structured Streaming -> Apache Kudu pipeline for ingestion. The main goal of the project is to aid customers in building a structured streaming application on CDH. For more information, visit Spark Structured Streaming Reference Application for CDH on GitHub.
Apache Sqoop
The following are some of the notable new features and enhancements in this release of Sqoop:
Support Decimal Type from Parquet Import and Export
Sqoop now supports the import and export of DECIMAL type correctly for both HDFS and Hive import. This feature is turned on by default in new CDH 6.2 clusters. It is turned off by default in older (upgraded) clusters.
Learn more at Configuring ADLS Access Using Cloudera Manager.
Importing Data into Microsoft Azure Data Lake Store (Gen1 and Gen2) Using Sqoop
CDH 6.2 supports using Apache Sqoop with both generations of ADLS. You can use Sqoop to efficiently transfer bulk data between Apache Hadoop and structured datastores such as relational databases. You can use Sqoop to import data from any relational database that has a JDBC adaptor such as SQL Server, MySQL, and others, to the ADLS file system.
For more information, see Importing Data into Microsoft Azure Data Lake Store Using Sqoop.
Apache Zookeeper
There are no notable new features in this release.