Cloudera Navigator Key Trustee Server Overview
Cloudera Navigator Key Trustee Server is an enterprise-grade virtual safe-deposit box that stores and manages cryptographic keys and other security artifacts. With Navigator Key Trustee Server, encryption keys are separated from the encrypted data, ensuring that sensitive data is still protected if unauthorized users gain access to the storage media.
Key Trustee Server protects these keys and other critical security objects from unauthorized access while enabling compliance with strict data security regulations. For added security, Key Trustee Server can integrate with a hardware security module (HSM). See Cloudera Navigator Key HSM Overview for more information.
In conjunction with the Key Trustee KMS, Navigator Key Trustee Server can serve as a backing key store for HDFS Transparent Encryption, providing enhanced security and scalability over the file-based Java KeyStore used by the default Hadoop Key Management Server.
Cloudera Navigator Encrypt also uses Key Trustee Server for key storage and management.
For instructions on installing Navigator Key Trustee Server, see Installing Cloudera Navigator Key Trustee Server. For instructions on configuring Navigator Key Trustee Server, see Initializing Standalone Key Trustee Server or Cloudera Navigator Key Trustee Server High Availability.
Key Trustee Server Architecture
Key Trustee Server is a secure object store. Clients register with Key Trustee Server, and are then able to store and retrieve objects with Key Trustee Server. The most common use case for Key Trustee Server is storing encryption keys to simplify key management and enable compliance with various data security regulations, but Key Trustee Server is agnostic about the actual objects being stored.
All interactions with Key Trustee Server occur over a TLS-encrypted HTTPS connection.
Key Trustee Server does not generate encryption keys for clients. Clients generate encryption keys, encrypt them with their private key, and send them over a TLS-encrypted connection to the Key Trustee Server. When a client needs to decrypt data, it retrieves the appropriate encryption key from Key Trustee Server and caches it locally to improve performance. This process is demonstrated in the following diagram:
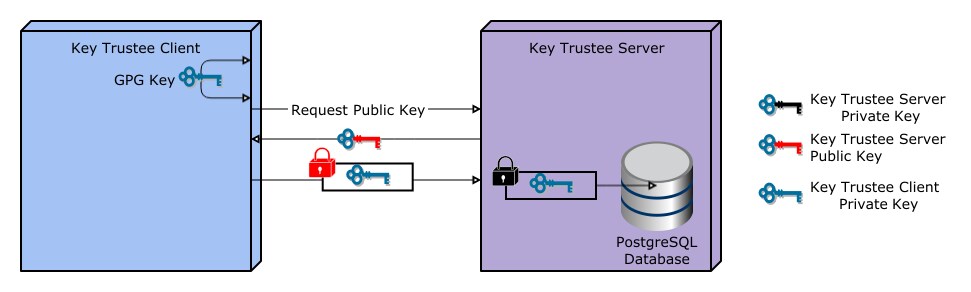
The most common Key Trustee Server clients are Navigator Encrypt and Key Trustee KMS.
When a Key Trustee client registers with Key Trustee Server, it generates a unique fingerprint. All client interactions with the Key Trustee Server are authenticated with this fingerprint. You must ensure that the file containing this fingerprint is secured with appropriate Linux file permissions. The file containing the fingerprint is /etc/navencrypt/keytrustee/ztrustee.conf for Navigator Encrypt clients, and /var/lib/kms-keytrustee/keytrustee/.keytrustee/keytrustee.conf for Key Trustee KMS.
Many clients can use the same Key Trustee Server to manage security objects. For example, you can have several Navigator Encrypt clients using a Key Trustee Server, and also use the same Key Trustee Server as the backing store for Key Trustee KMS (used in HDFS encryption).