Cloudera Navigator Auditing Architecture
Cloudera Navigator auditing provides data auditing and access features. The Cloudera Navigator auditing architecture is illustrated below.
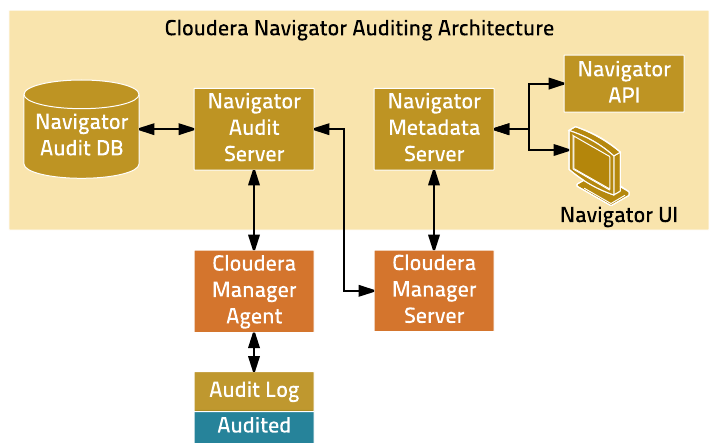
When Cloudera Navigator auditing is configured, plug-ins that enable collection and filtering of service access events are added to the HDFS, HBase, and Hive (that is, the HiveServer2 and Beeswax servers) services. The plug-ins write the events to an audit log on the local filesystem. The existence of the plug-ins places requirements on these services when Cloudera Navigator is upgraded. Cloudera Impala, Sentry, and the Cloudera Navigator Metadata Server collect and filter access events and write them to an audit log file.
The Cloudera Manager Agent monitors the audit log files and sends the events to the Navigator Audit Server. The Cloudera Manager Agent retries any event that it fails to transmit. As there is no in-memory transient buffer involved, once the events are written to the audit log file, they are guaranteed to be delivered (as long as filesystem is available). The Cloudera Manager Agent keeps track of current event offset in the audit log that it has successfully transmitted, so on any crash/restart it picks up the event from the last successfully sent position and resumes. Audit logs are rotated and the Cloudera Manager Agent follows the rotation of the log. The Agent also takes care of purging old audit logs once they have been successfully transmitted to the Navigator Audit Server. If a plug-in fails to write an event to the audit log file, it can either drop the event or shut down the process in which they are running (depending on the configured queue policy).
- Tracking and coalescing events
- Storing events to the audit database