The Sentry Service
The Sentry service is a RPC server that stores the authorization metadata in an underlying relational database and provides RPC interfaces to retrieve and manipulate privileges. It supports secure access to services using Kerberos. The service serves authorization metadata from the database backed storage; it does not handle actual privilege validation. The Hive and Impala services are clients of this service and will enforce Sentry privileges when configured to use Sentry.
The motivation behind introducing a new Sentry service is to make it easier to handle user privileges than the existing policy file approach. Providing a database instead, allows you to use the more traditional GRANT/REVOKE statements to modify privileges.
Continue reading:
For more information on installing, upgrading and configuring the Sentry service, see:
Prerequisites
- CDH 5.1.x (or higher) managed by Cloudera Manager 5.1.x (or higher). See the Cloudera Manager Administration Guide and Cloudera Installation Guide for instructions.
- HiveServer2 and the Hive Metastore running with strong authentication. For HiveServer2, strong authentication is either Kerberos or LDAP. For the Hive Metastore, only Kerberos is considered strong authentication (to override, see Securing the Hive Metastore).
- Impala 1.4.0 (or higher) running with strong authentication. With Impala, either Kerberos or LDAP can be configured to achieve strong authentication.
- Implement Kerberos authentication on your cluster. For instructions, see Enabling Kerberos Authentication Using the Wizard.
Privilege Model
With CDH 5.1, the privilege model has undergone changes to accommodate the new grant/revoke syntax that is used with the Sentry service. These changes are common to both the new database-backed Sentry service, as well as the previous policy file approach.
- Allows any user to execute show function, desc function, and show locks.
- Allows the user to see only those tables and databases for which this user has privileges.
- Requires a user to have the necessary privileges on the URI to execute HiveQL operations that take in a location. Examples of such operations include LOAD, IMPORT, and EXPORT.
For more information, see Appendix: Authorization Privilege Model for Hive and Impala.
Users and Groups
- A user is an entity that is permitted by the authentication subsystem to access the Hive service. This entity can be a Kerberos principal, an LDAP userid, or an artifact of some other pluggable authentication system supported by HiveServer2.
- A group connects the authentication system with the authorization system. It is a collection of one or more users who have been granted one or more authorization roles. Sentry allows a set of roles to be configured for a group.
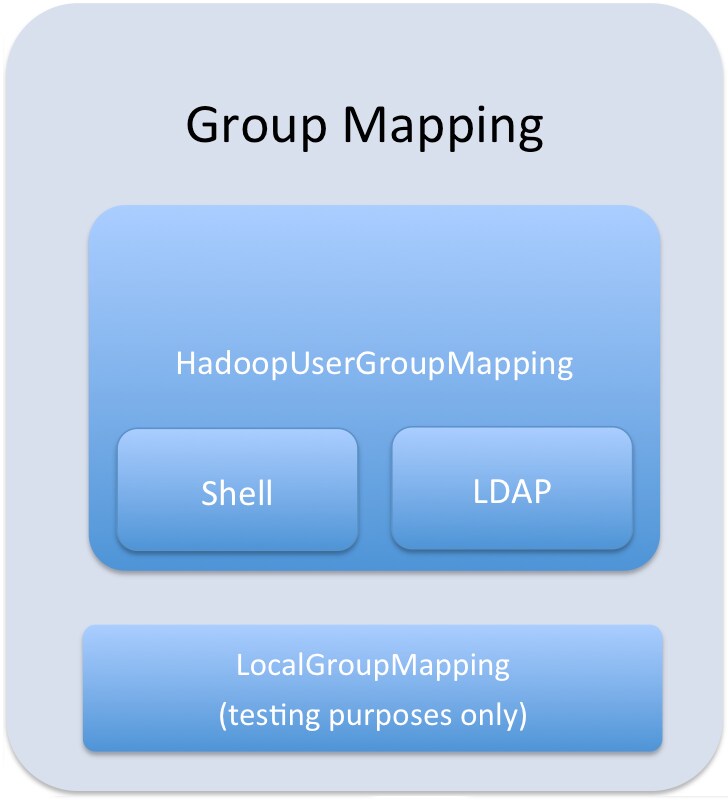
- A configured group provider determines a user’s affiliation with a group. The current release supports HDFS-backed groups and locally configured groups.
analyst = sales_reporting, data_export, audit_reportHere the group analyst is granted the roles sales_reporting, data_export, and audit_report. The members of this group can run the HiveQL statements that are allowed by these roles. If this is an HDFS-backed group, then all the users belonging to the HDFS group analyst can run such queries.
Continue reading:
Configuring User to Group Mappings
Minimum Required Role: Configurator (also provided by Cluster Administrator, Full Administrator)
- Go to the Hive service.
- Click the Configuration tab.
- Under the Service-Wide category, go to the Sentry section.
- Set the Sentry User to Group Mapping Class property to org.apache.sentry.provider.file.HadoopGroupResourceAuthorizationProvider.
- Click Save Changes.
- Restart the Hive service.
Appendix: Authorization Privilege Model for Hive and Impala
Privileges can be granted on different objects in the Hive warehouse. Any privilege that can be granted is associated with a level in the object hierarchy. If a privilege is granted on a container object in the hierarchy, the base object automatically inherits it. For instance, if a user has ALL privileges on the database scope, then (s)he has ALL privileges on all of the base objects contained within that scope.
Object Hierarchy in Hive
Server
Database
Table
Partition
Columns
View
Index
Function/Routine
Lock
| Privilege | Object |
|---|---|
| INSERT | DB, TABLE |
| SELECT | DB, TABLE |
| ALL | SERVER, TABLE, DB, URI |
- hdfs://host:port/directory_A/directory_B
- hdfs://host:port/directory_A/directory_B/directory_C
- hdfs://host:port/directory_A/directory_B/directory_C/directory_D
- hdfs://host:port/directory_A/directory_B/directory_E
| Base Object | Granular privileges on object | Container object that contains the base object | Privileges on container object that implies privileges on the base object |
|---|---|---|---|
| DATABASE | ALL | SERVER | ALL |
| TABLE | INSERT | DATABASE | ALL |
| TABLE | SELECT | DATABASE | ALL |
| VIEW | SELECT | DATABASE | ALL |
| Operation | Scope | Privileges | URI | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CREATE DATABASE | SERVER | ALL | ||
| DROP DATABASE | DATABASE | ALL | ||
| CREATE TABLE | DATABASE | ALL | ||
| DROP TABLE | TABLE | ALL | ||
| CREATE VIEW | DATABASE; SELECT on TABLE | ALL | SELECT on TABLE | |
| DROP VIEW | VIEW/TABLE | ALL | ||
| CREATE INDEX | TABLE | ALL | ||
| DROP INDEX | TABLE | ALL | ||
| ALTER TABLE .. ADD COLUMNS | TABLE | ALL | ||
| ALTER TABLE .. REPLACE COLUMNS | TABLE | ALL | ||
| ALTER TABLE .. CHANGE column | TABLE | ALL | ||
| ALTER TABLE .. RENAME | TABLE | ALL | ||
| ALTER TABLE .. SET TBLPROPERTIES | TABLE | ALL | ||
| ALTER TABLE .. SET FILEFORMAT | TABLE | ALL | ||
| ALTER TABLE .. SET LOCATION | TABLE | ALL | URI | |
| ALTER TABLE .. ADD PARTITION | TABLE | ALL | ||
| ALTER TABLE .. ADD PARTITION location | TABLE | ALL | URI | |
| ALTER TABLE .. DROP PARTITION | TABLE | ALL | ||
| ALTER TABLE .. PARTITION SET FILEFORMAT | TABLE | ALL | ||
| SHOW TBLPROPERTIES | TABLE | SELECT/INSERT | ||
| SHOW CREATE TABLE | TABLE | SELECT/INSERT | ||
| SHOW PARTITIONs | TABLE | SELECT/INSERT | ||
| DESCRIBE TABLE | TABLE | SELECT/INSERT | ||
| DESCRIBE TABLE .. PARTITION | TABLE | SELECT/INSERT | ||
| LOAD DATA | TABLE | INSERT | URI | |
| SELECT | TABLE | SELECT | ||
| INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE | TABLE | INSERT | ||
| CREATE TABLE .. AS SELECT | DATABASE; SELECT on TABLE | ALL | SELECT on TABLE | |
| USE <dbName> | Any | |||
| ALTER TABLE .. SET SERDEPROPERTIES | TABLE | ALL | ||
| ALTER TABLE .. PARTITION SET SERDEPROPERTIES | TABLE | ALL | ||
| Hive-Only Operations | ||||
| INSERT OVERWRITE DIRECTORY | TABLE | INSERT | URI | |
| Analyze TABLE | TABLE | SELECT + INSERT | ||
| IMPORT TABLE | DATABASE | ALL | URI | |
| EXPORT TABLE | TABLE | SELECT | URI | |
| ALTER TABLE TOUCH | TABLE | ALL | ||
| ALTER TABLE TOUCH PARTITION | TABLE | ALL | ||
| ALTER TABLE .. CLUSTERED BY SORTED BY | TABLE | ALL | ||
| ALTER TABLE .. ENABLE/DISABLE | TABLE | ALL | ||
| ALTER TABLE .. PARTITION ENABLE/DISABLE | TABLE | ALL | ||
| ALTER TABLE .. PARTITION.. RENAME TO PARTITION | TABLE | ALL | ||
| ALTER DATABASE | DATABASE | ALL | ||
| DESCRIBE DATABASE | DATABASE | SELECT/INSERT | ||
| SHOW COLUMNS | TABLE | SELECT/INSERT | ||
| SHOW INDEXES | TABLE | SELECT/INSERT | ||
| GRANT PRIVILEGE | Allowed only for Sentry admin users | |||
| REVOKE PRIVILEGE | Allowed only for Sentry admin users | |||
| SHOW GRANT | Allowed only for Sentry admin users | |||
| ADD JAR | Not Allowed | |||
| ADD FILE | Not Allowed | |||
| DFS | Not Allowed | |||
| Impala-Only Operations | ||||
| EXPLAIN | TABLE | SELECT | ||
| INVALIDATE METADATA | SERVER | ALL | ||
| INVALIDATE METADATA <table name> | TABLE | SELECT/INSERT | ||
| REFRESH <table name> | TABLE | SELECT/INSERT | ||
| CREATE FUNCTION | SERVER | ALL | ||
| DROP FUNCTION | SERVER | ALL | ||
| COMPUTE STATS | TABLE | ALL | ||