Managing Metadata Extraction
The metadata extracted from various cluster services is used to support many other Cloudera Navigator features and functions, such as its ability to render lineage diagrams. The metadata extraction feature can be selectively enabled or disabled for supported services. Obsolete and deleted metadata should be regularly purged from the system to facilitate fast search and noise-free lineage diagrams. These tasks are discussed in the following topics.
Enabling and Disabling Metadata Extraction
Minimum Required Role: Navigator Administrator (also provided by Full Administrator)
Enabling Hive Metadata Extraction in a Secure Cluster
The Navigator Metadata Server authenticates to the Hive Metastore (HMS) using the hue user account. By default, the hue account can connect to the HMS.
However, if the Hive service Hive Metastore Access Control and Proxy User Groups Override property or the HDFS service Hive Proxy User Groups property have been changed from their defaults, user hue may be prevented from authenticating to the Hive Metastore and metadata cannot be extracted from Apache Hive.
If this is the case, modify the Hive service Hive Metastore Access Control and Proxy User Groups Override property or the HDFS service Hive Proxy User Groups property as follows:
- Go to the Hive or HDFS service.
- Click the Configuration tab.
- In the Search box, type proxy.
- In the Hive service Hive Metastore Access Control and Proxy User Groups Override (or the HDFS service Hive Proxy User Groups property), click the plus-icon to add a new row. The property applies to the default role group but can be applied to other role groups as needed. See Modifying Configuration Properties Using Cloudera Manager.
- Type hue.
- Click Save Changes.
- Restart the Cloudera Navigator service.
Enabling Spark Metadata Extraction
- Log in to Cloudera Manager Admin Console.
- Search for the configuration setting "config.navigator.lineage_enabled" or "navigator_lineage_enabled" to display the current setting:
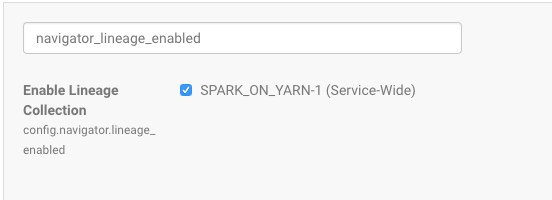
- To disable lineage collection, click the checked box (or leave as is to keep it enabled).
If the cluster was upgraded from a previous release of Cloudera Navigator and an Advanced Configuration Snippet (Safety Valve) was used to enable lineage, you must remove that snippet to avoid conflict with the new Enable Lineage Collection property. Using a safety valve to enable Spark metadata extraction has been deprecated.
- Log in to the Cloudera Manager Admin Console.
- Select .
- Click the Configuration tab.
- Select .
- For Filter Category, click Advanced.
- Scroll to the Navigator Metadata Server Advanced Configuration Snippet (Safety Valve) for cloudera-navigator.properties setting.
- Remove any deprecated setting for Spark extraction, such as:
nav.spark.extraction.enable
- Click Save Changes.
- Restart the Navigator Metadata Server role.
Using the Purge APIs for Metadata Maintenance Tasks
Required Role: Cloudera Navigator Full Administrator
The volume of metadata maintained by Navigator Metadata Server can grow quickly and exceed the capacity of the Solr instance that processes the index and supports the search capability. For faster search and cleaner lineage tracing, use the purge feature to routinely delete unwanted metadata from the system.
Purging stale metadata is also recommended prior to upgrading an existing Cloudera Navigator instance. See Avoiding Out-of-Memory Errors During an Upgrade for details.
Purging Metadata for HDFS Entities, Hive and Impala Select Queries, and YARN, Sqoop, and Pig Operations
You can delete metadata for HDFS entities, Hive and Impala select queries, and YARN, Sqoop and Pig operations by using the purge method. (Metadata for Hive tables is not deleted.) Purge is a long-running task that requires exclusive access to the Solr instance and does not allow any concurrent activities, including extraction.
- Back up the Navigator Metadata Server storage directory.
- Invoke the http://fqdn-n.example.com:port/api/APIversion/maintenance/purge endpoint with the following parameters:
For example, the following call purges the metadata of all deleted HDFS entities because the elapsed minutes value is set to 0:
Purge Parameters Metadata Parameter Description HDFS deleteTimeThresholdMinutes After an HDFS entity is deleted, the number of minutes that must pass before that entity can be purged. Default: 86400 minutes (60 days).
runtimeCapMinutes Number of minutes that the HDFS purge can run. When this limit is reached, the purge state is saved and the purge task terminates. You must run the purge again to purge any remaining entities. If you set the value to 0, no HDFS files or directories are purged.
Default: 720 minutes (12 hours).
Hive and Impala Select Queries; YARN, Sqoop, Pig Operations deleteSelectOperations Boolean. If set to true, the purge deletes all Hive and Impala select queries, and YARN, Sqoop, and Pig operations, that are older than the number of days defined by the staleQueryThresholdDays value. Default: false
staleQueryThresholdDays For Hive and Impala select queries, and YARN, Sqoop, and Pig operations, the number of days they must be older than to be purged. To disable purge for Hive and Impala select queries, and for YARN, Sqoop, and Pig operations, set the threshold to a very large value, for example, 36500.
Default: 60 days
$ curl -X POST -u admin:admin "http://fqdn-n.example.com:port/api/APIversion/maintenance/purge?deleteTimeThresholdMinutes=0"
Purge tasks do not start until all currently running extraction tasks finish.
- When all tasks have completed, click Continue to return to the Cloudera Navigator UI.
Retrieving Purge Status
curl -X GET -u admin:admin "http://fqdn-n.example.com:port/api/APIversion/maintenance/running"
[{
"id" : 5,
"type" : "PURGE",
"startTime" : "2016-03-10T23:17:41.884Z",
"endTime" : "1970-01-01T00:00:00.000Z",
"status" : "IN_PROGRESS",
"message" : "Purged 2661984 out of 4864714 directories. Averaging 1709 directories per minute.",
"username" : "admin",
"stage" : "HDFS_DIRECTORIES",
"stagePercent" : 54
}]
Retrieving Purge History
To view the purge history, invoke the http://fqdn-n.example.com:port/api/APIversion/maintenance/history endpoint with the following parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| offset | First purge history entry to retrieve.
Default: 0. |
| limit | Number of history entries to retrieve from the offset.
Default: 100. |
curl -X GET -u admin:admin "http://fqdn-n.example.com:port/api/APIversion/maintenance/history?offset=0&limit=100"A result would look similar to:
[
{
"id": 1,
"type": "PURGE",
"startTime": "2016-03-09T18:57:43.196Z",
"endTime": "2016-03-09T18:58:33.337Z",
"status": "SUCCESS",
"username": "admin",
"stagePercent": 0
},
{
"id": 2,
"type": "PURGE",
"startTime": "2016-03-09T19:47:39.401Z",
"endTime": "2016-03-09T19:47:40.841Z",
"status": "SUCCESS",
"username": "admin",
"stagePercent": 0
},
{
"id": 3,
"type": "PURGE",
"startTime": "2016-03-10T01:27:39.632Z",
"endTime": "2016-03-10T01:27:46.809Z",
"status": "SUCCESS",
"username": "admin",
"stagePercent": 0
},
{
"id": 4,
"type": "PURGE",
"startTime": "2016-03-10T01:57:40.461Z",
"endTime": "2016-03-10T01:57:41.174Z",
"status": "SUCCESS",
"username": "admin",
"stagePercent": 0
},
{
"id": 5,
"type": "PURGE",
"startTime": "2016-03-10T23:17:41.884Z",
"endTime": "2016-03-10T23:18:06.802Z",
"status": "SUCCESS",
"username": "admin",
"stagePercent": 0
}
]Configuring Display of Inputs and Outputs
- Log in to the Cloudera Manager Admin Console.
- Select .
- Click the Configuration tab.
- Select .
- In Navigator Metadata Server Advanced Configuration Snippet (Safety Valve) for cloudera-navigator.properties, set the property
nav.ui.details_io_enabled=true
To apply this configuration property to other role groups as needed, edit the value for the appropriate role group. See Modifying Configuration Properties Using Cloudera Manager.
- Click Save Changes.
- Restart the Navigator Metadata Server role.