Cloudera Navigator Data Management
- Auditing—Verify that access permissions are appropriate and audit all user accesses to data stored in the cluster, in HDFS and Hive metastores
- Lineage and provenance—Trace data back to its source and track downstream dependencies
- Discovery and exploration—Review, customize, and update metadata about the objects contained in the cluster, and find available data through powerful search and lineage capabilities
- Lifecycle management—Define policies that facilitate data migration
Given the range of features, Cloudera Navigator data management can meet the needs of data curators, business intelligence analysts, administrators, data scientists, application developers, among others.
For example, data stewards and data engineers using Hadoop clusters want better self-service data discovery. They want to be able to find all the data associated with particular projects by looking for meaningful labels (managed metadata, custom metadata) without needing to know all about the low-level structures within the cluster. They can define practical business metadata using the Managed Metadata feature:
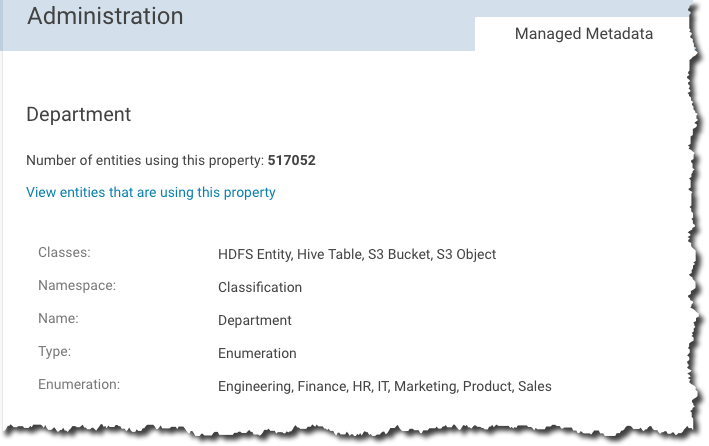
By defining policies, the tagging of data entities with the appropriate metadata as it is consumed in the cluster can be automated. This is just one example of Cloudera Navigator at work. The product also lets data stewards and analysts identify trends and trace lineage of any data entity to its source, so they can best leverage the data contained in the cluster for actionable insight.
Many of Cloudera Navigator's features are not limited to data stewards, governance, and analyst audiences. System administrators can glean meaningful information about data operations
that might be tying up system resources. For example, say an organization's business users complain to an admin one day that query response times have been a problem since early May. The
administrator uses Cloudera Navigator console to take a look at to look at the Activity Summary page, which provides a comprehensive overall view—databases created, tables created, tables dropped, SQL queries started, and so on. Looking
for trends, the administrator navigates to the Data Explorer tab, makes two selections to filter for the past several weeks on SQL Queries Started as source type and gleans some clues about a rogue
SQL query.
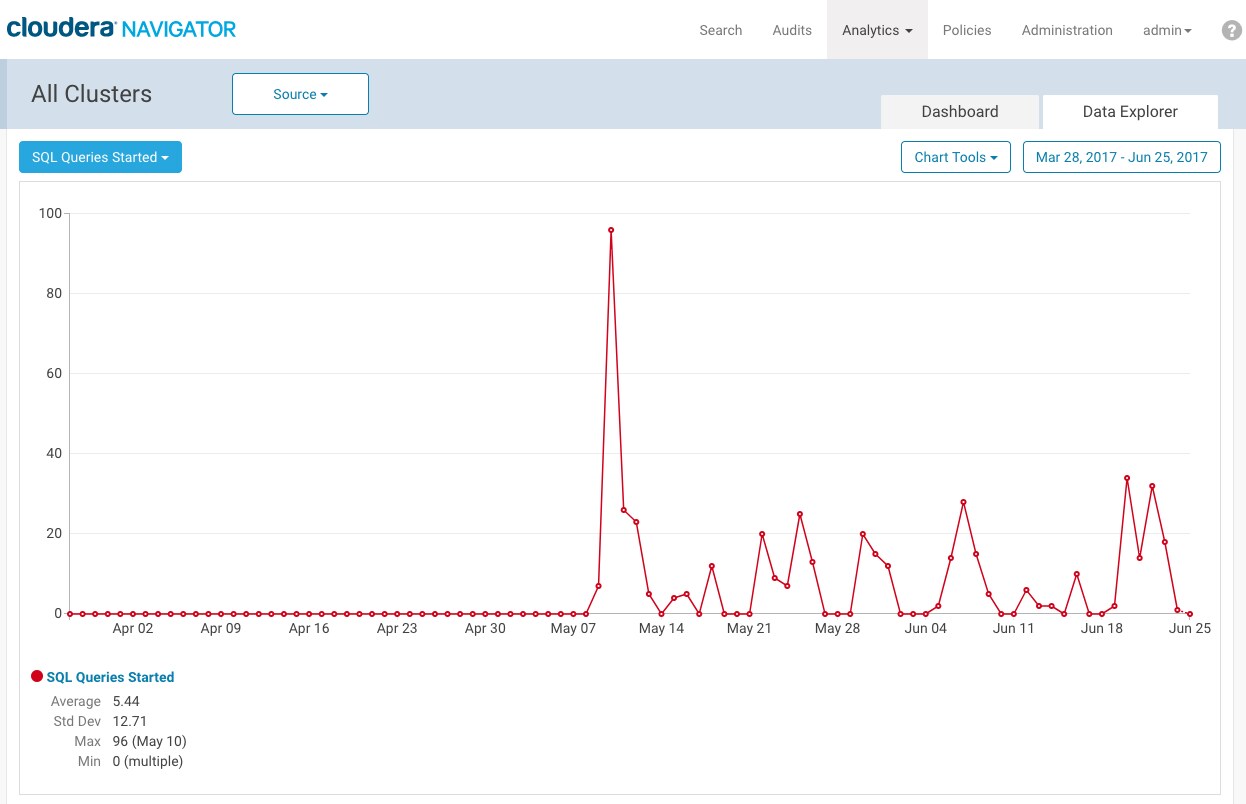
With further drill-down, the administrator identifies the source of the problem for fast resolution. See Data Stewardship Dashboard for more information.
These are just two examples of the features and functions of Cloudera Navigator detailed in this guide. This guide focuses on using the Cloudera Navigator console for the core capabilities provided, such as gathering audit reports, defining business metadata for the system, exploring metadata for system, tracing lineage of data entities to their sources, defining policies that target specific entities for specific processing, and so on—all the capabilities needed by data stewards, auditors, compliance teams, data analysts, and the like.