Introduction
This tutorial walks you through the process of creating, resizing, and terminating Data Hubs on the Cloudera on cloud.
In order to save the end user time and cost, Data Hubs can be provisioned, resized, or disposed of quickly in response to rapidly changing workloads.
Prerequisites
- Must have administrator access to an already created environment on Cloudera on cloud.
Outline
- Concepts
- Create data hub
- Access services on data hub
- Terminate data hub cluster
- Summary
- Further reading
The videos below provide a brief overview of what this tutorial covers:
Concepts
The following concepts are key to understanding Data Hub:
Workload clusters
All Data Hub clusters are workload clusters. These clusters are created for running specific workloads such as data engineering or data analytics.
Cluster definitions
A cluster definition is a reusable cluster template in JSON format that can be used for creating multiple Data Hub clusters with identical cloud provider settings.
Cluster templates
Data Hub uses cluster templates for defining cluster topology: defining host groups and components installed on each host group.
Recipes
A recipe is a script that runs on all nodes of a selected host group at a specific time. You can use recipes for tasks such as installing additional software or performing advanced cluster configuration. For example, you can use a recipe to put a JAR file on the Hadoop classpath.
Custom properties
Custom properties are configuration properties that can be set on a Cloudera Runtime cluster, but Data Hub allows you to conveniently set these during cluster creation.
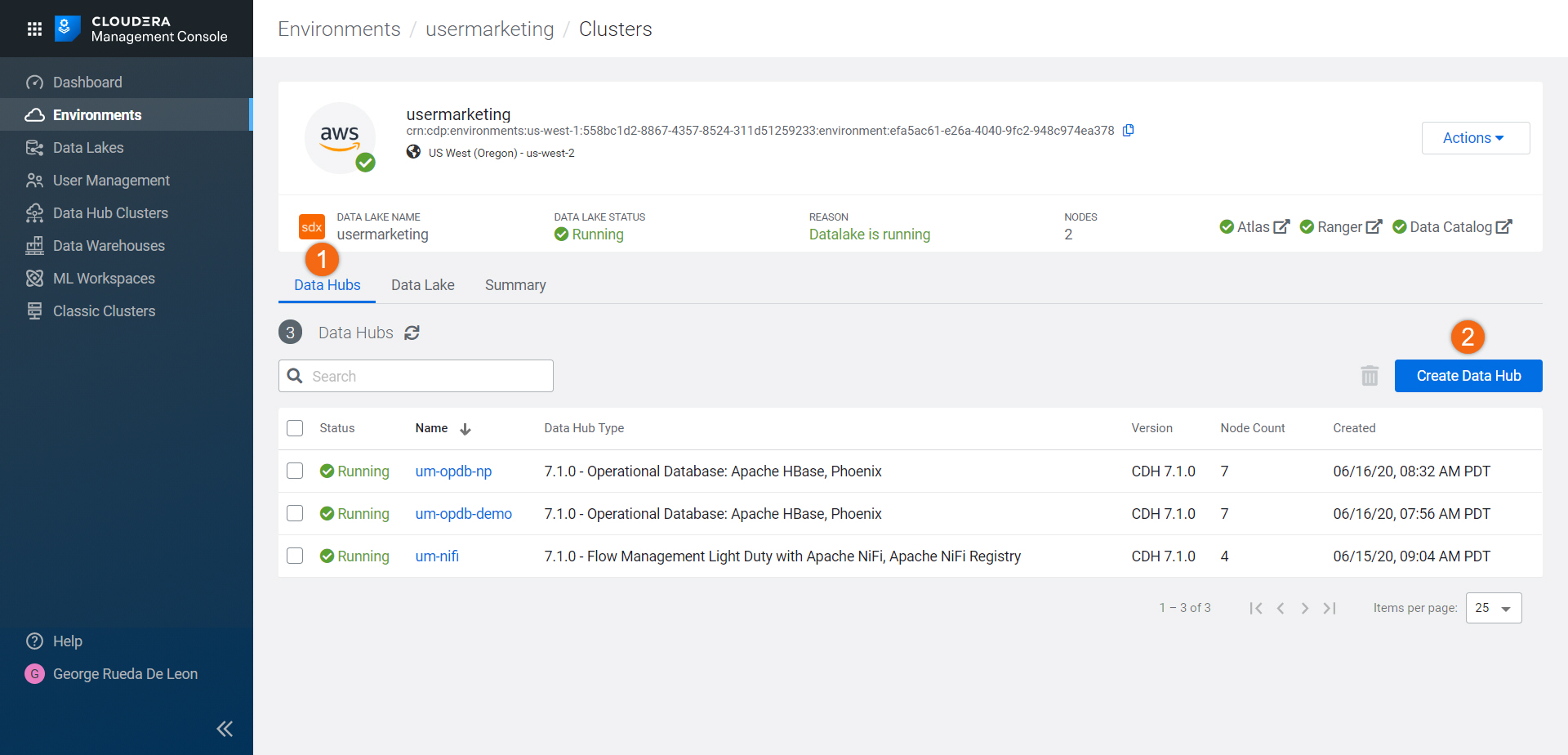
In the Environments section, search for the environment you want to create a Data Hub and click on its name:
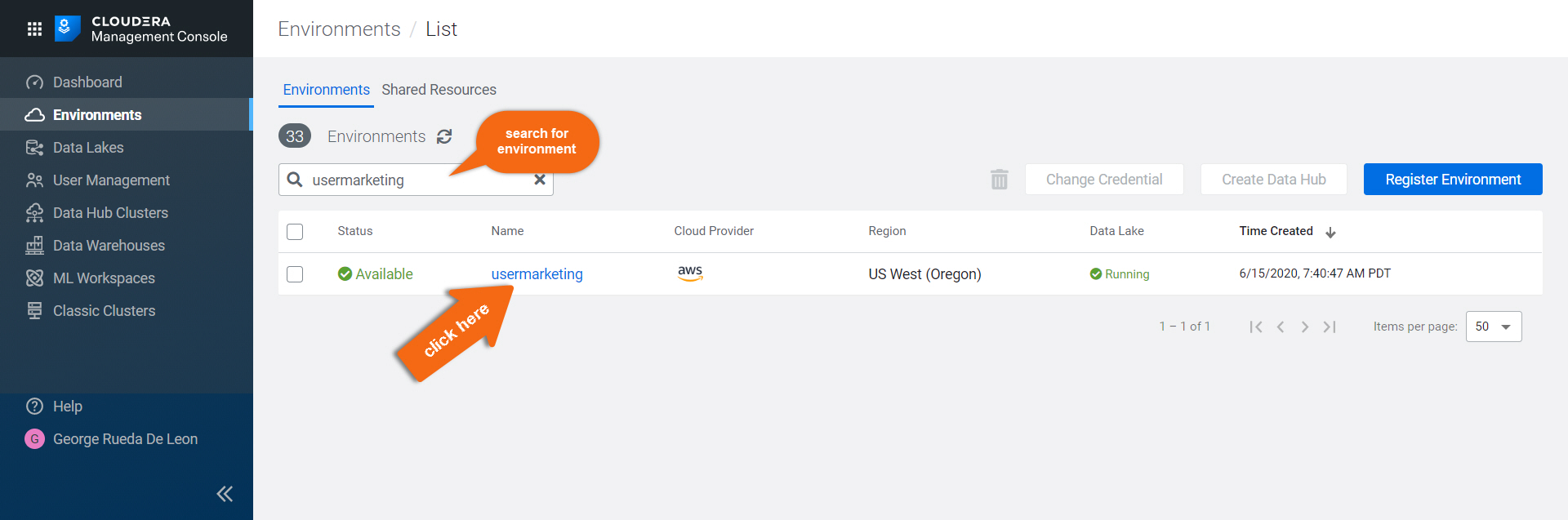
- Select Data Hubs to see all the data hub clusters created in the environment
- Since we are creating a new data hub, click on Create Data Hub
You need to choose from two(2) options for provisioning this Data Hub:
- Cluster Definition
Choose one of the prescriptive cluster definitions predefined by CDP - Custom
Choose a previously created, custom cluster definition
In this tutorial, we will choose Cluster Definition, which provides a large selection of predefined cluster definitions:
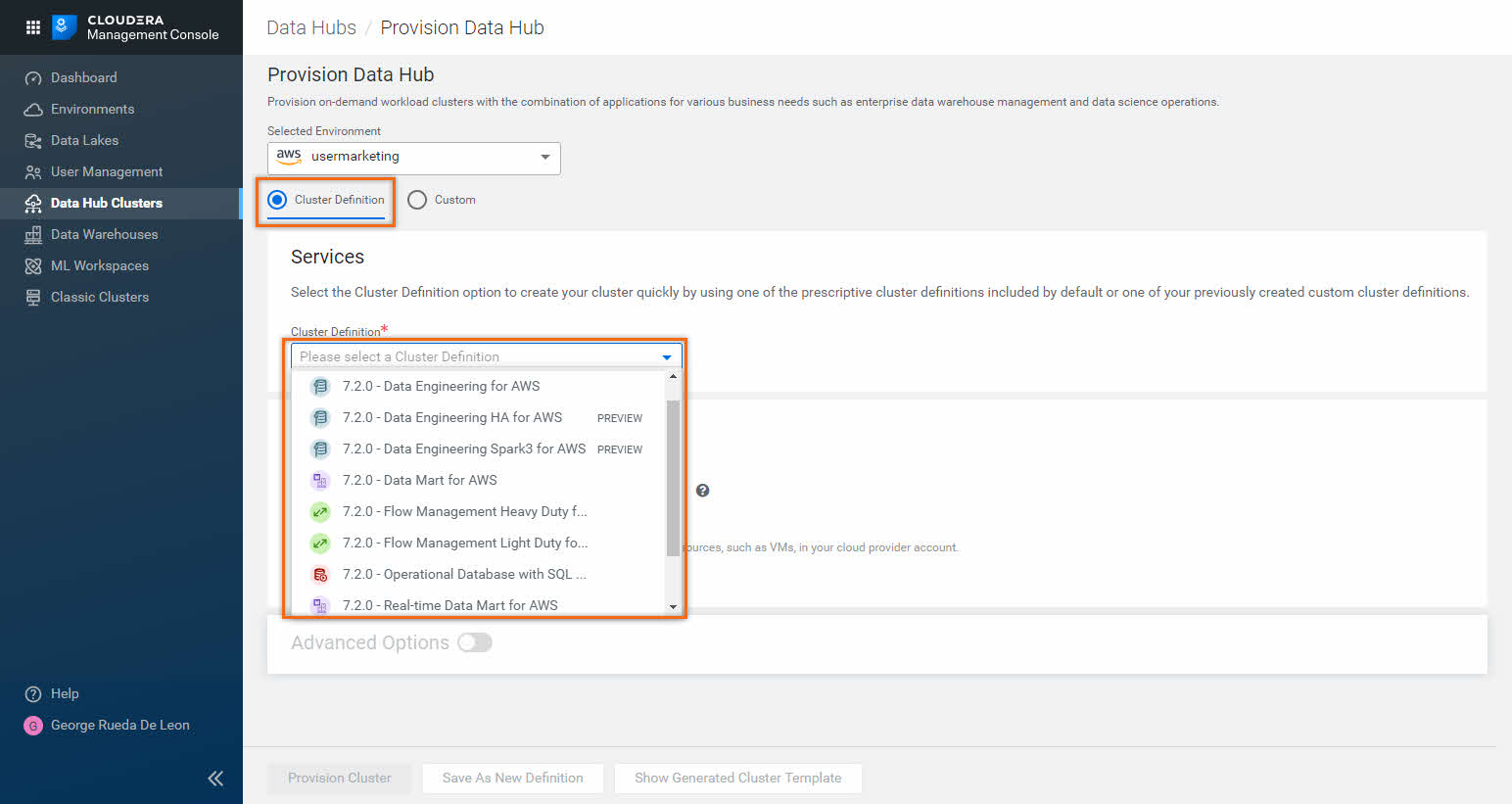
Note: Your CDP environment may have different cluster definitions.
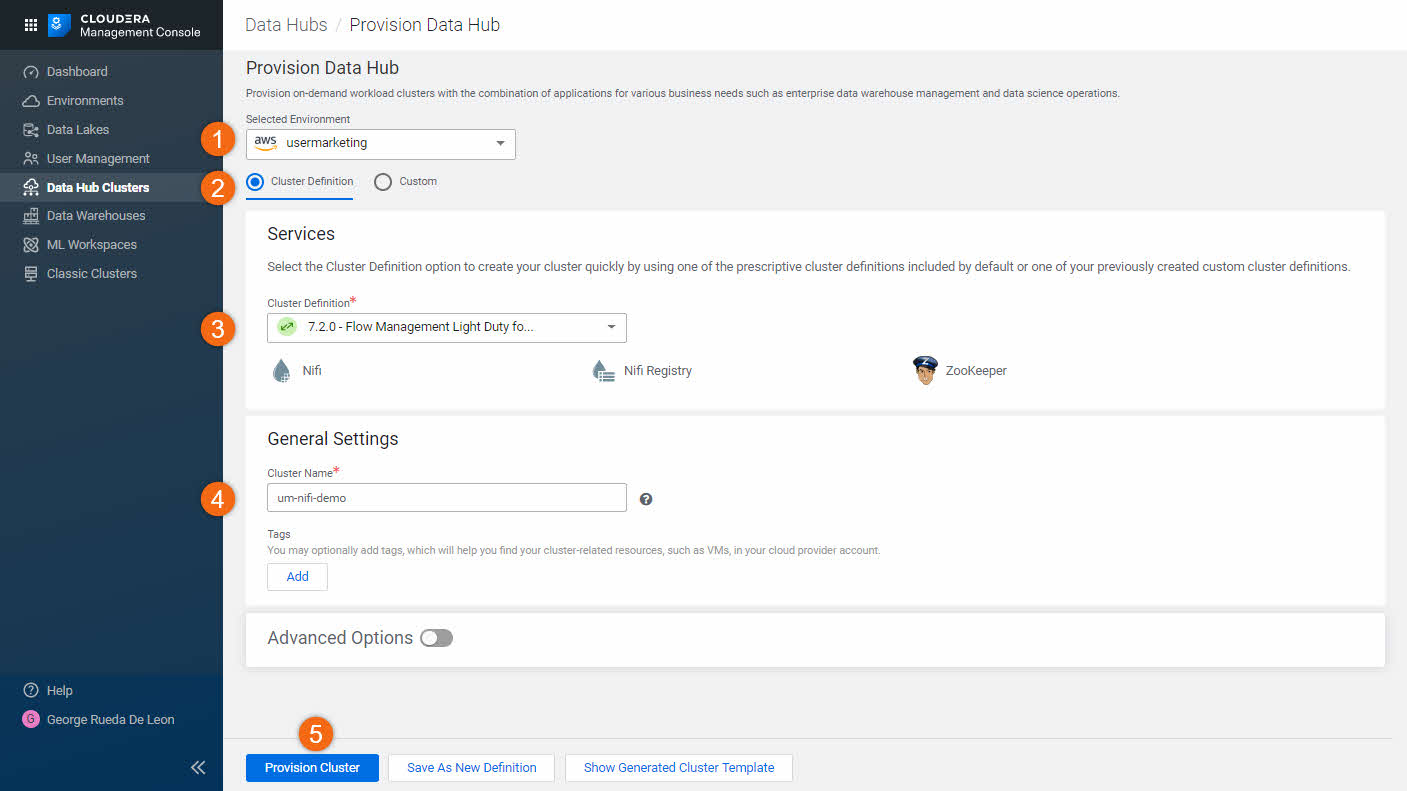
Let's complete the data hub provisioning form:
- Selected Environment:
usermarketing - Choose the radio button: Cluster Definition
- Cluster Definition:
7.2.0 - Flow Management Light Duty for AWS - Cluster Name:
um-nifi-demo
At this point, you may do step 5. Provision Cluster to complete the provisioning.
We suggest to review Advanced Options prior to provisioning.
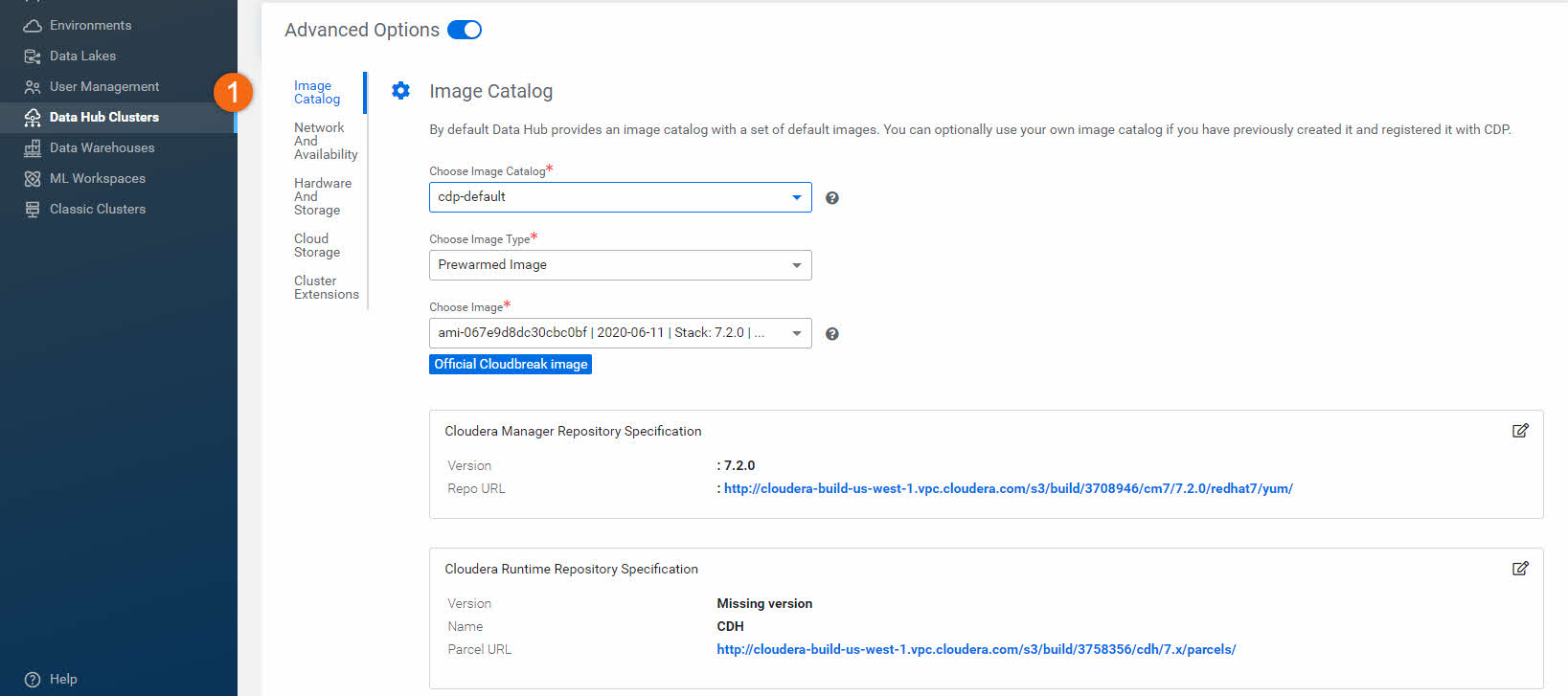
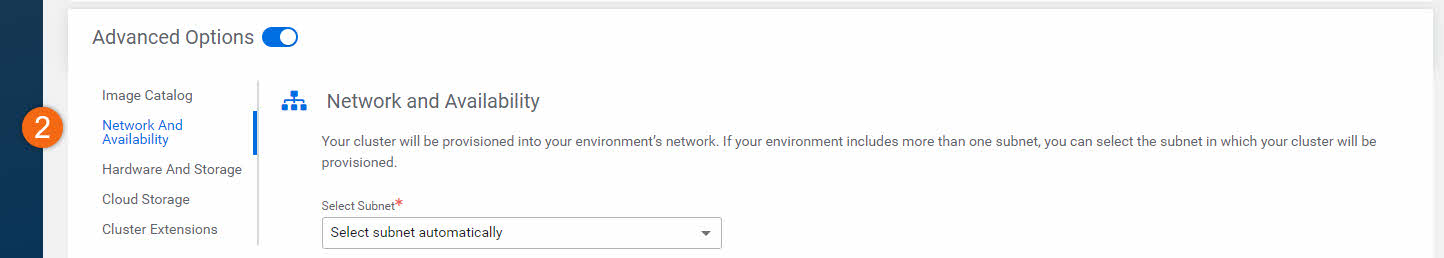
- Network And Availability: Allows you to customize the networking settings of your cluster. If your environment includes more than one subnet, you can select the subnet in which your cluster will be provisioned.
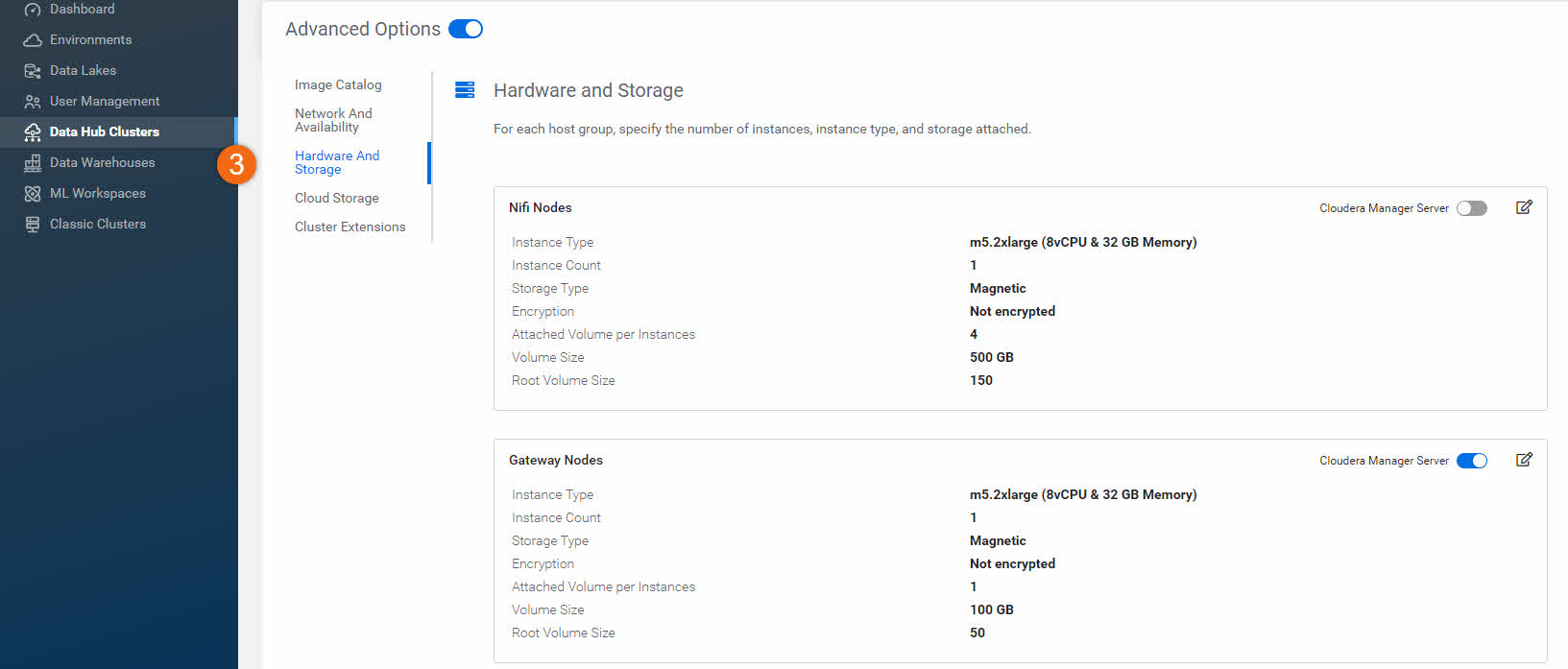
- Hardware And Storage: Allows you to customize the cloud provider specific clusters hardware and storage.
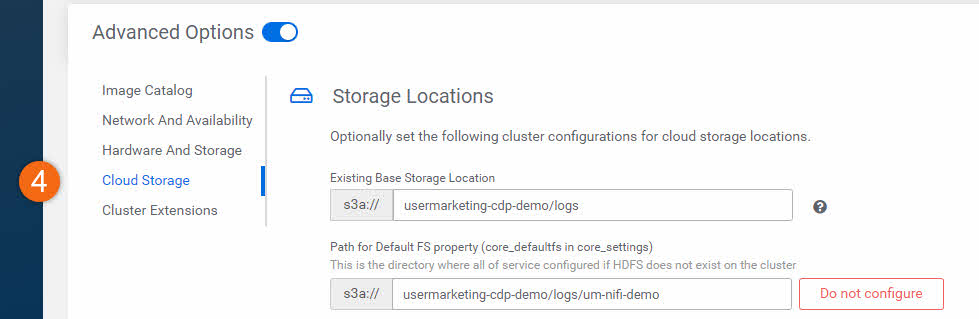
- Cloud Storage: Allows you to optionally specify the base storage location. By default, it inherits storage location settings from when the environment was created.
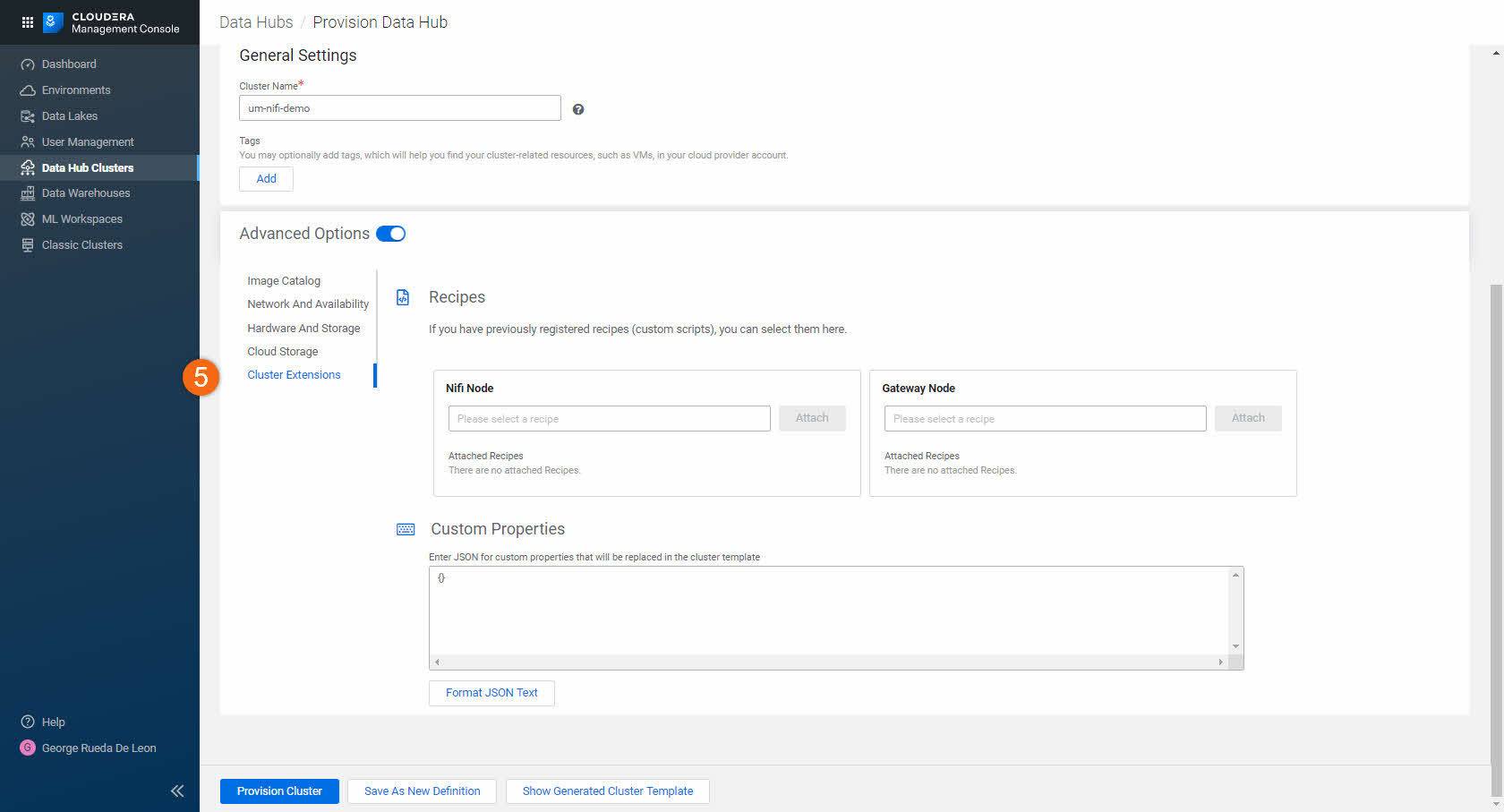
- Cluster Extensions:
Recipes are scripts that run on all nodes of a selected host group at a specific time. Available recipe execution times are:
- Before Cloudera Manager server starts
- Before cluster termination
- After Cloudera Manager server starts
- After cluster installation
All registered recipes are located in:
Environments > Shared Resources > Recipes.
Custom Properties: Allows you to configure properties that can be set on a Cloudera Runtime cluster, but Data Hub allows you to conveniently set it during cluster creation.
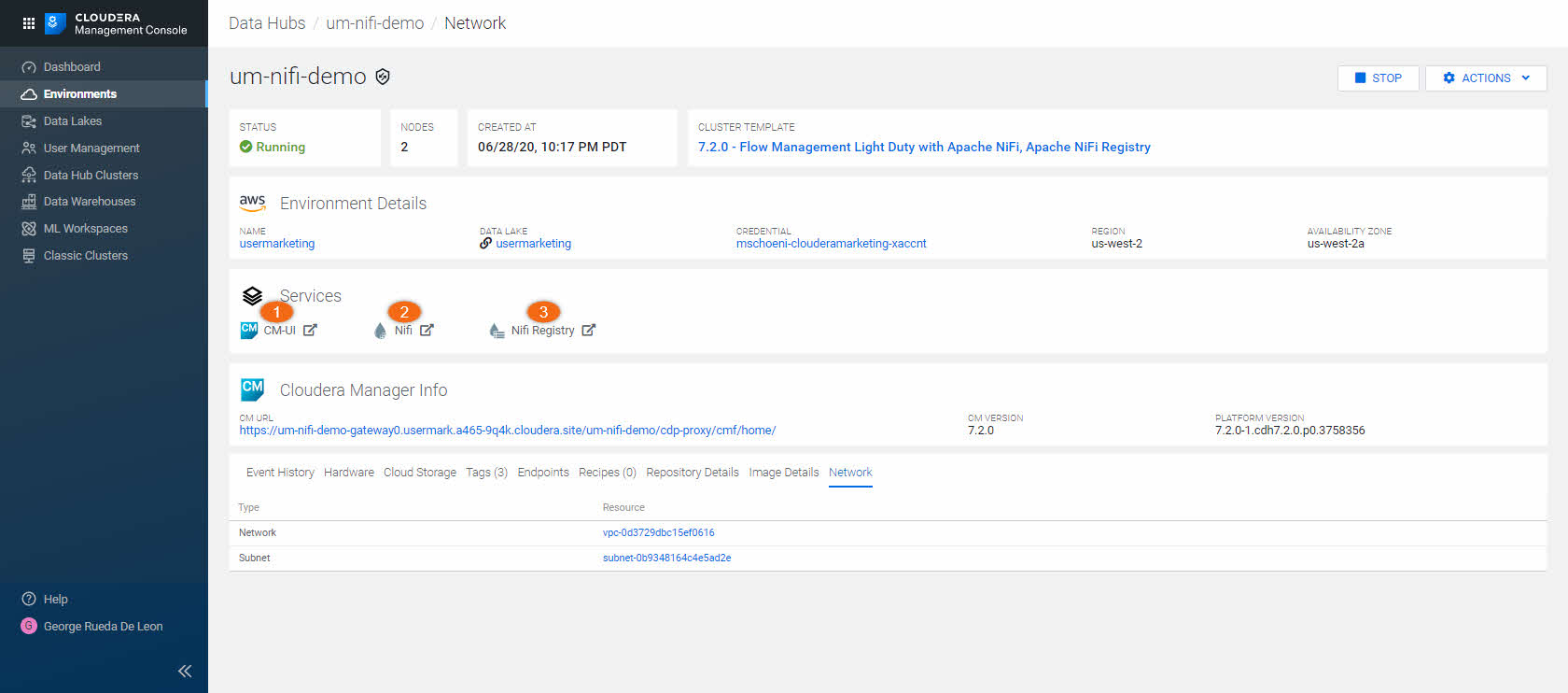
The list of services available depend on the Cluster Definition chosen. As you recall, we chose Cluster Definition: 7.2.0 - Flow Management Light Duty for AWS, which provides three(3) services:
- Cloudera Manager
- NiFi
- NiFi Registry
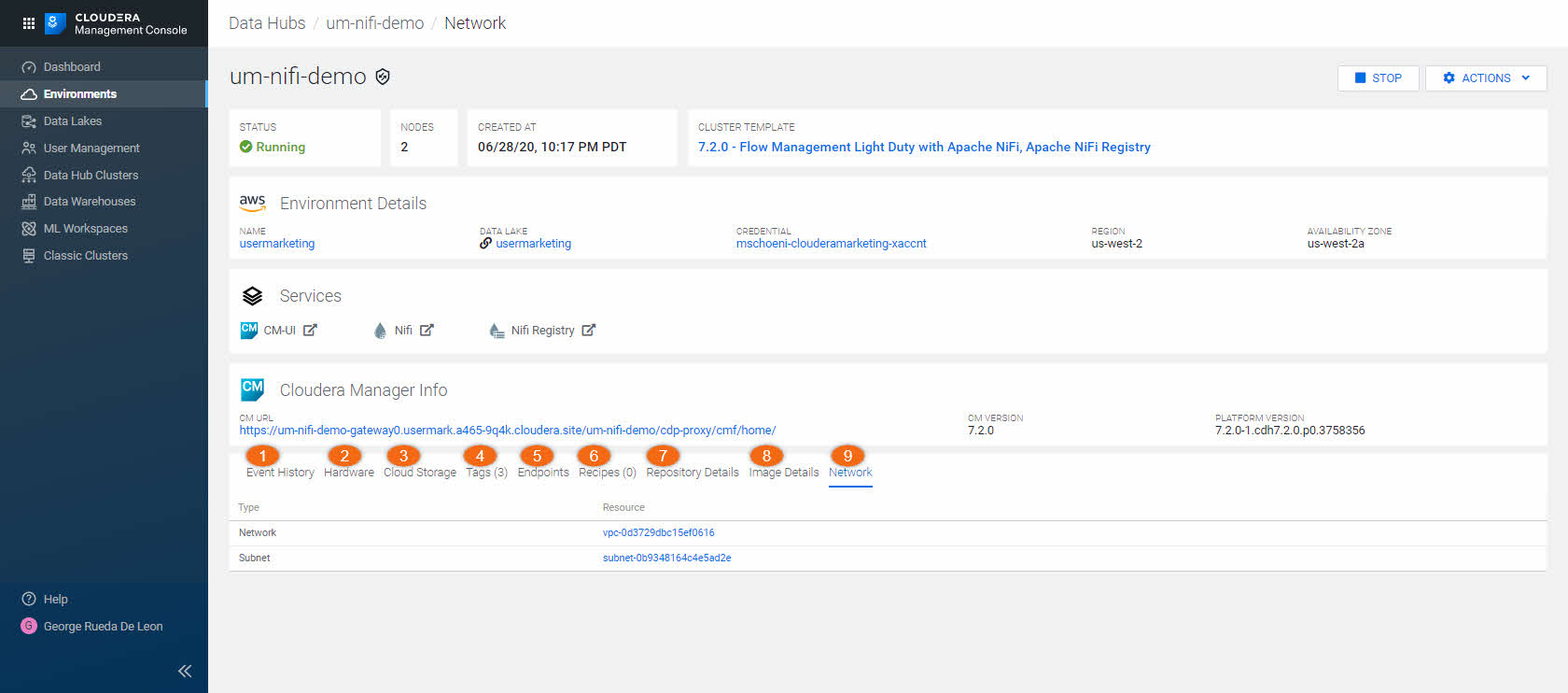
There are nine (9) tabs to explore:
- Event History:
Shows events logged for the cluster, with the most recent event at the top. The Download option allows you to download the event history.
- Hardware:
Displays information about your cluster instances: instance names, instance IDs, instance types, their status, fully qualified domain names (FQDNs), and private and public IPs.
- Cloud Storage:
Displays cloud storage locations for certain properties.
- Tags:
Displays key and value pair(s) of the user-defined tags.
- Endpoints:
Displays the URL for all cluster API endpoints.
- Recipes:
Displays recipe-related information. For each recipe, you can see the host group on which a recipe was executed, recipe name, and recipe type.
- Repository Details:
Displays Cloudera Manager and Cloudera Runtime repository information, as you provided when creating a cluster.
- Image Details:
Displays information about the image catalog used and its location.
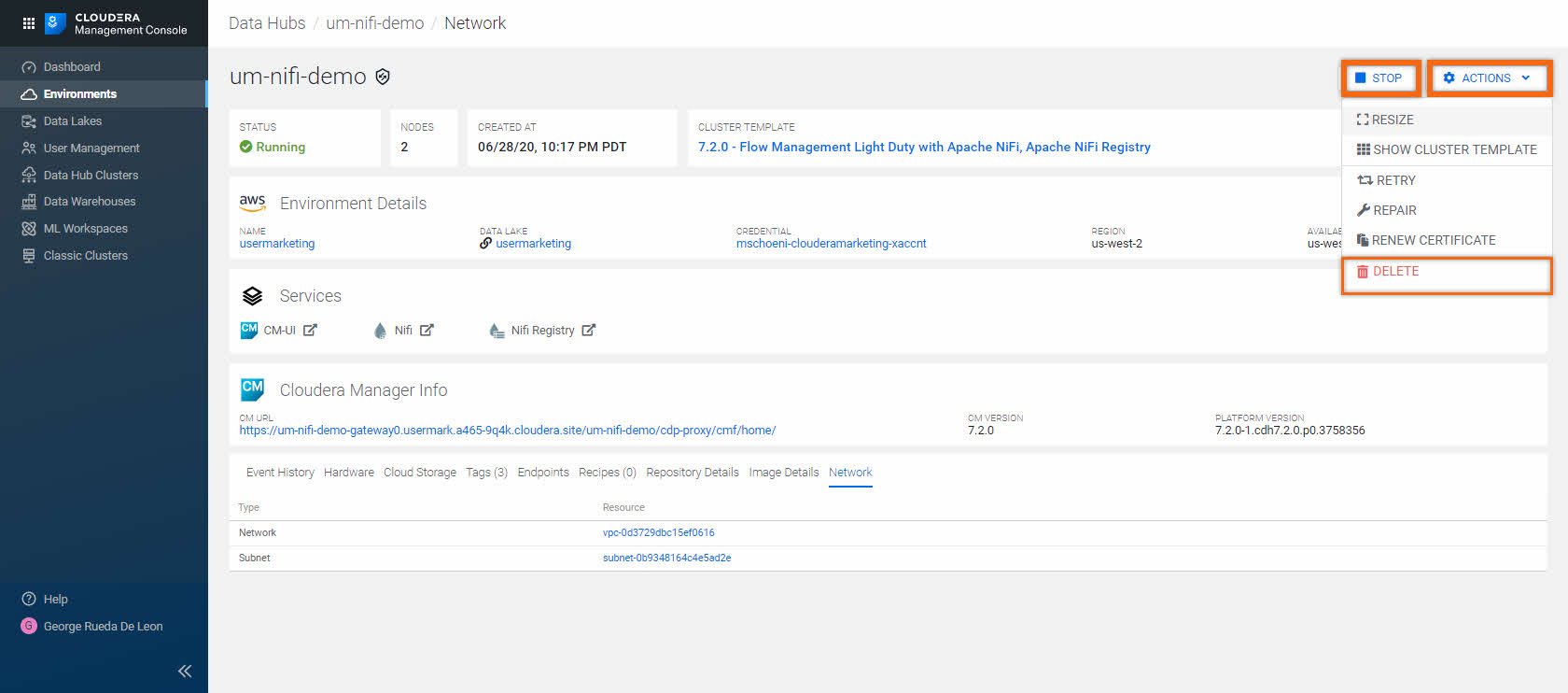
- Network:
Displays information about the names of the network and subnet in which the cluster is running and the links to related cloud provider console.
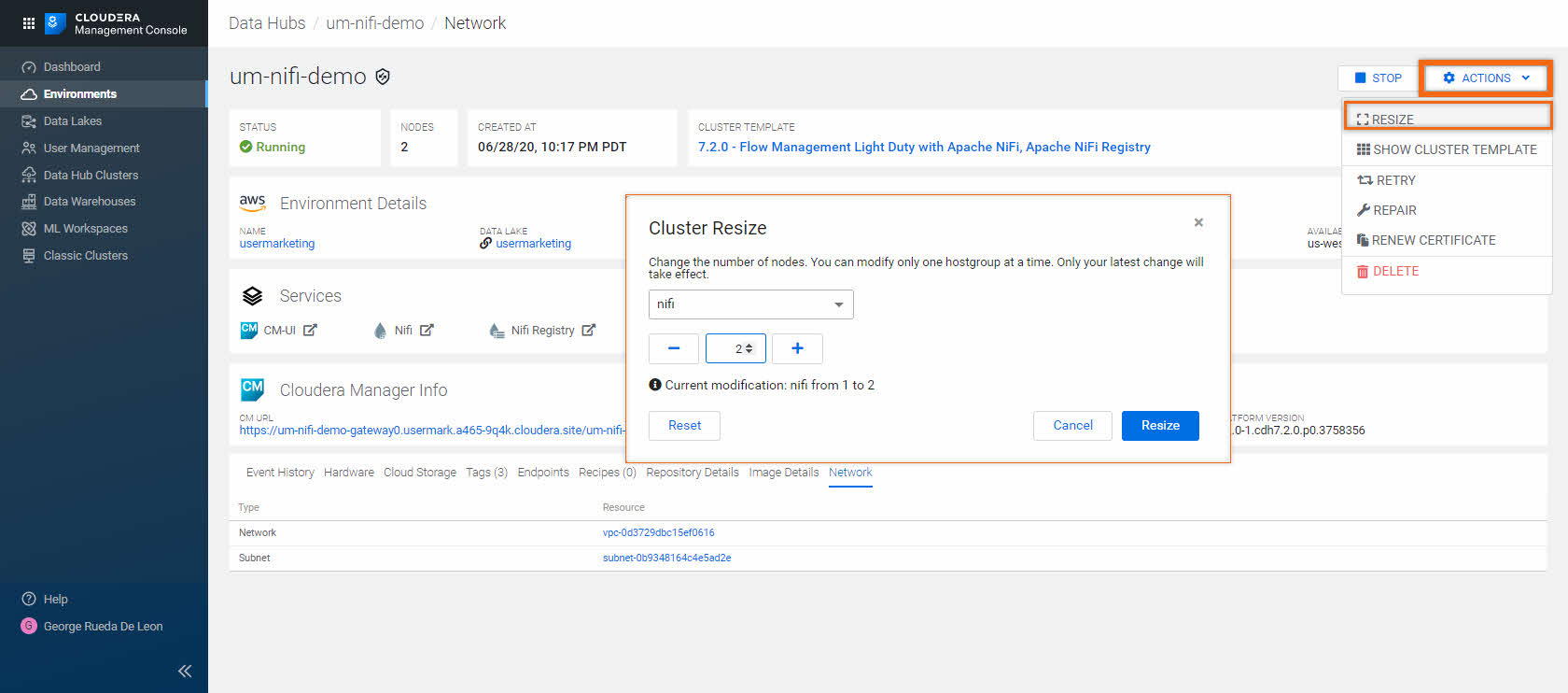
Terminate data hub cluster
When you decide that this Data Hub is no longer needed, you may either STOP or DELETE the Data Hub cluster:
- To STOP the Data Hub cluster, click on STOP
When you are ready to restart, click on START
- To terminate/delete/destroy the Data Hub cluster, click ACTIONS > DELETE
Once initiated, there’s no way to undo