Bucket Layouts in Apache Ozone
Are you struggling to manage the ever-increasing volume and variety of data in today’s constantly evolving landscape of modern data architectures? The vast tapestry of data types spanning structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data means data professionals need to be proficient with various data formats such as ORC, Parquet, Avro, CSV, and Apache Iceberg tables, to cover the ever growing spectrum of datasets – be they images, videos, sensor data, or other type of media content. Navigating this intricate maze of data can be challenging, and that’s why Apache Ozone has become a popular, cloud-native storage solution that spans any data use case with the performance needed for today’s data architectures.
Apache Ozone, a highly scalable, high performance distributed object store, provides the ideal solution to this requirement with its bucket layout flexibility and multi-protocol support. Apache Ozone is compatible with Amazon S3 and Hadoop FileSystem protocols and provides bucket layouts that are optimized for both Object Store and File system semantics. With these features, Apache Ozone can be used as a pure object store, a Hadoop Compatible FileSystem (HCFS), or both, enabling users to store different types of data in a single store and access the same data using multiple protocols providing the scale of an object store and the flexibility of the Hadoop File system.
A previous blog post describes the different bucket layouts available in Ozone. This blog post is intended to provide guidance to Ozone administrators and application developers on the optimal usage of the bucket layouts for different applications.
To start with, Ozone’s namespace includes the following conceptual entities:
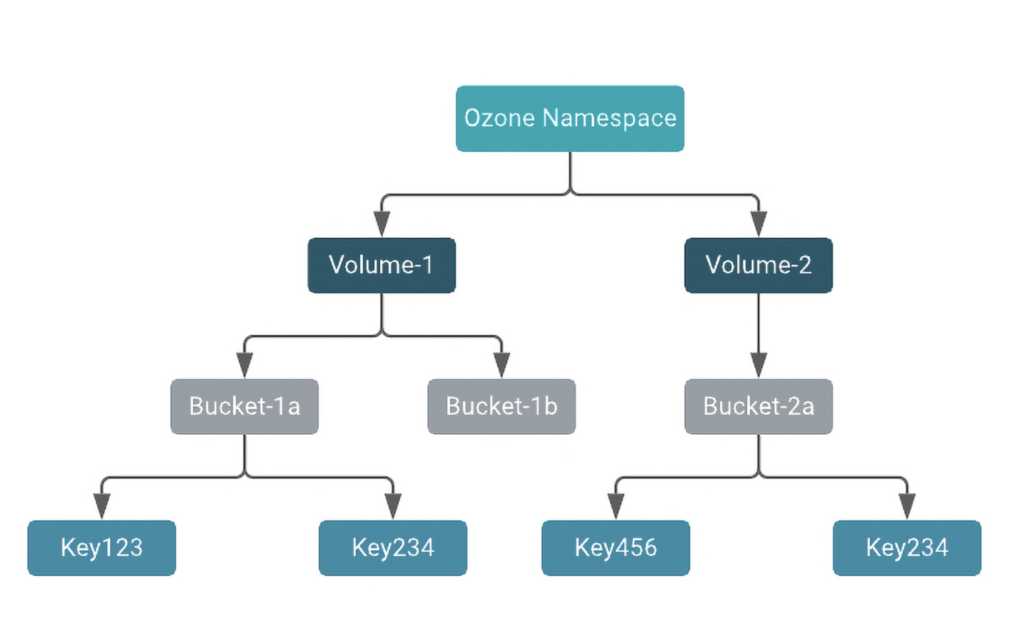 Fig.1 Apache Ozone Namespace layout
Fig.1 Apache Ozone Namespace layout
- Volumes are the top level namespace grouping in Ozone. Volume names must be unique and can be used for tenants or users.
- Buckets can be used as parent directories. Each volume can contain multiple buckets of data. Bucket names must be unique within a volume.
- Keys store data inside buckets. Keys can be files, directories, or objects.
Bucket Layouts in Apache Ozone
File System Optimized (FSO) and Object Store (OBS) are the two new bucket layouts in Ozone for unified and optimized storage as well as access to files, directories, and objects. Bucket layouts provide a single Ozone cluster with the capabilities of both a Hadoop Compatible File System (HCFS) and Object Store (like Amazon S3). One of these two layouts should be used for all new storage needs.
A description of the bucket layouts and their features are below.
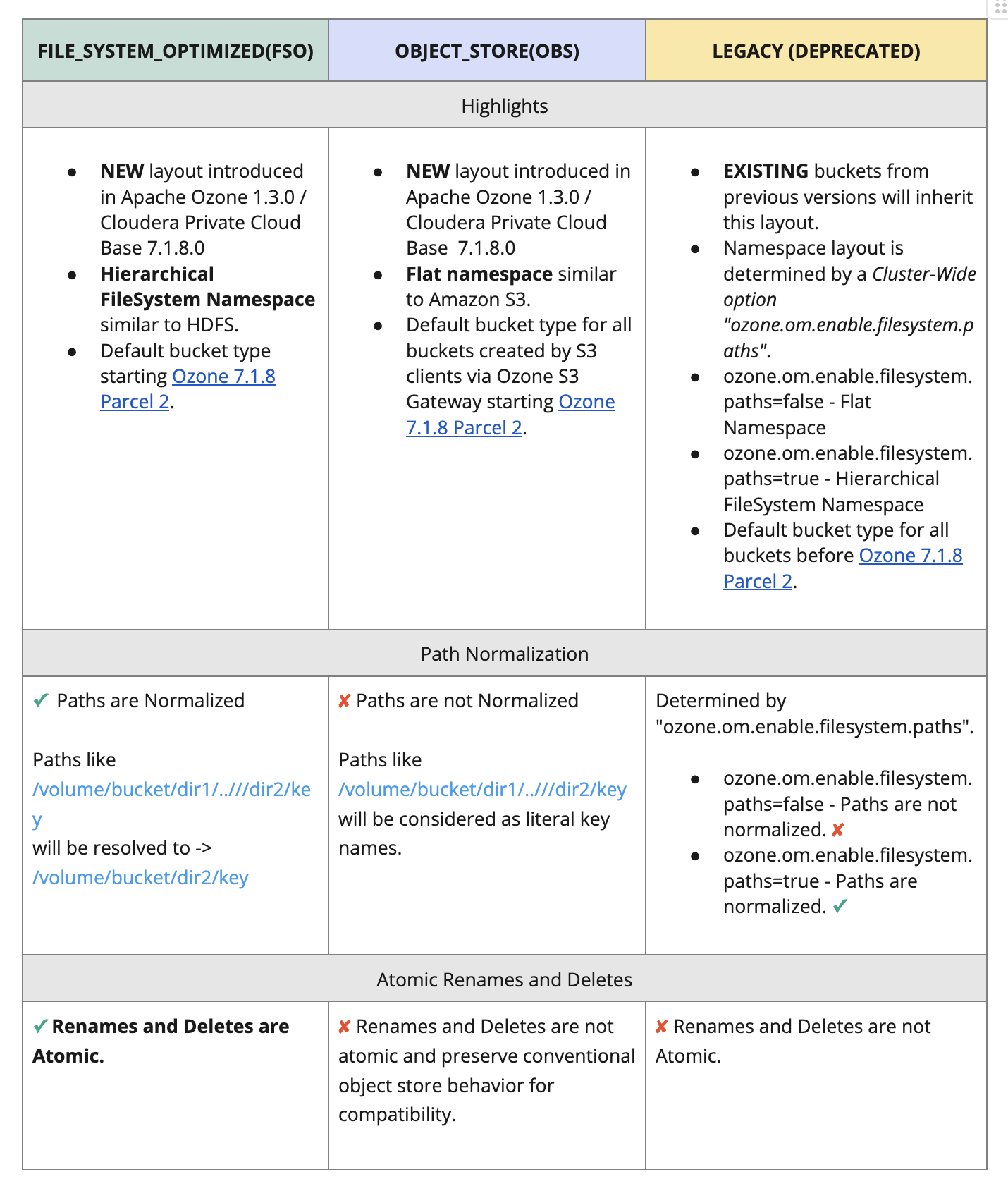 Fig 2. Bucket Layouts in Apache Ozone
Fig 2. Bucket Layouts in Apache Ozone
Interoperability between FS and S3 API
Users can store their data in Apache Ozone and can access the data with multiple protocols.
Protocols provided by Ozone:
- ofs
- ofs is a Hadoop Compatible File System (HCFS) protocol.
- ozone fs is a command line interface similar to “hdfs dfs” CLI that works with HCFS protocols like ofs.
- Most traditional analytics applications like Hive, Spark, Impala, YARN etc. are built to use the HCFS protocol natively and hence they can use the ofs protocol to access Ozone out of the box with no changes.
- Trash implementation is available with the ofs protocol to ensure safe deletion of objects.
- S3
- Any cloud-native S3 workload built to access S3 storage using either the AWS CLI, Boto S3 client, or other S3 client library can access Ozone via the S3 protocol.
- Since Ozone supports the S3 API, it can also be accessed using the s3a connector. S3a is a translator from the Hadoop Compatible Filesystem API to the Amazon S3 REST API.
- Hive, Spark, Impala, YARN, BI tools with S3 connectors can interact with Ozone using the s3a protocol.
- When accessing FSO buckets through the S3 interface, paths are normalized, but renames and deletes are not atomic.
- s3a will translate directory renames to individual object renames at the client before sending them to Ozone. Ozone’s S3 gateway will forward the object renames to the FSO bucket.
- Access to LEGACY buckets using S3 interface is the same as access to FSO bucket if, ozone.om.enable.filesystem.paths=true otherwise, it’s the same as access to OBS bucket.
- o3
- Ozone Shell (ozone sh) is a command line interface used to interact with Ozone using the o3 protocol.
- Ozone Shell is recommended to use for volume and bucket management, but it can also be used to read and write data.
- Only expected to be used by cluster administrators.
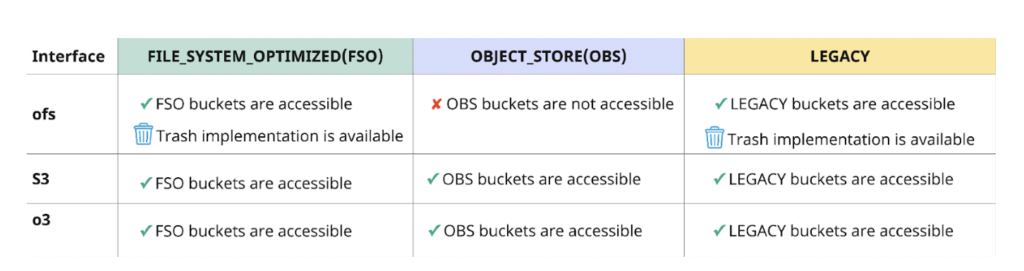 Fig 3. Interoperability between FS and S3 APIOzone’s support for interoperability between File System and Object Store API can facilitate the implementation of hybrid cloud use cases such as:
Fig 3. Interoperability between FS and S3 APIOzone’s support for interoperability between File System and Object Store API can facilitate the implementation of hybrid cloud use cases such as:
1- Ingesting data using S3 interface into FSO buckets for low latency analytics using the ofs protocol.
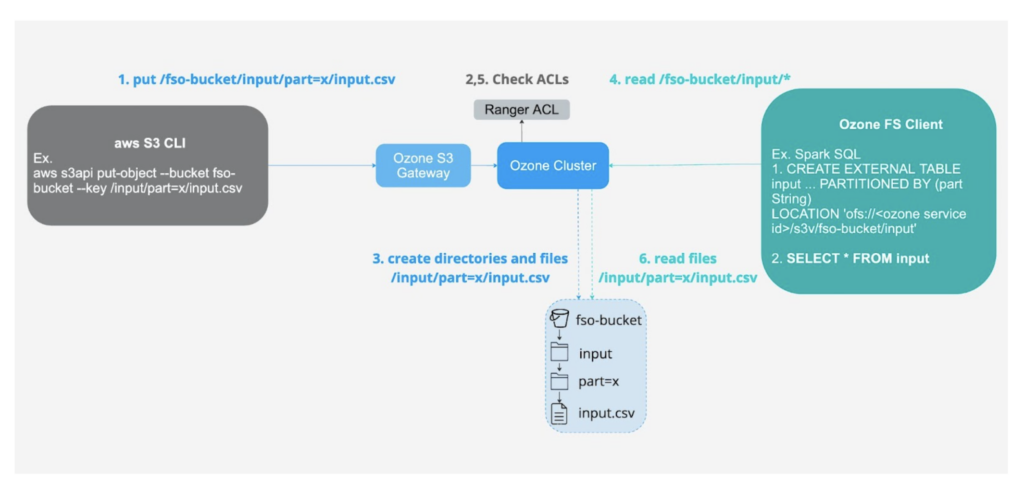 Fig 4. Ingest using S3 API and consume using FS API
Fig 4. Ingest using S3 API and consume using FS API
2- Storing data on-premises for security and compliance which can also be accessed using cloud-compatible API.
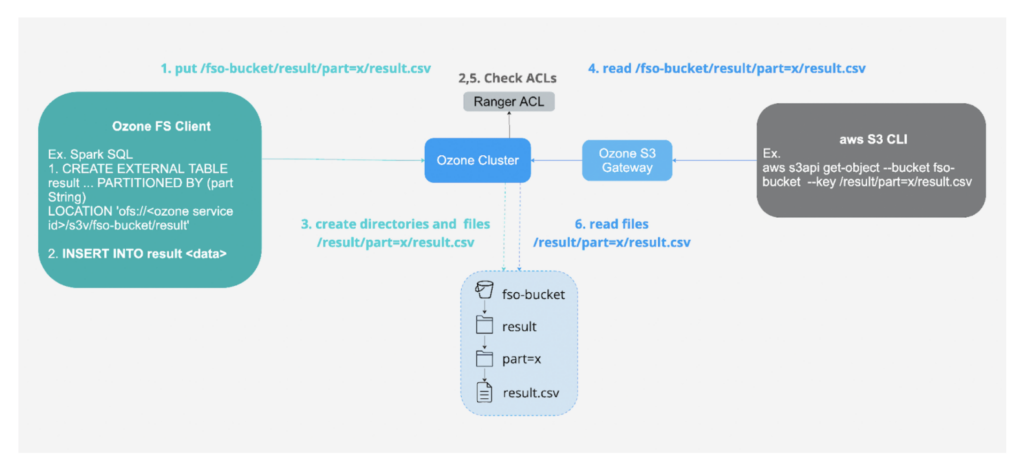 Fig 5. Ingest using FS API and consume using S3 API
Fig 5. Ingest using FS API and consume using S3 API
When to use FSO vs OBS Bucket Layouts
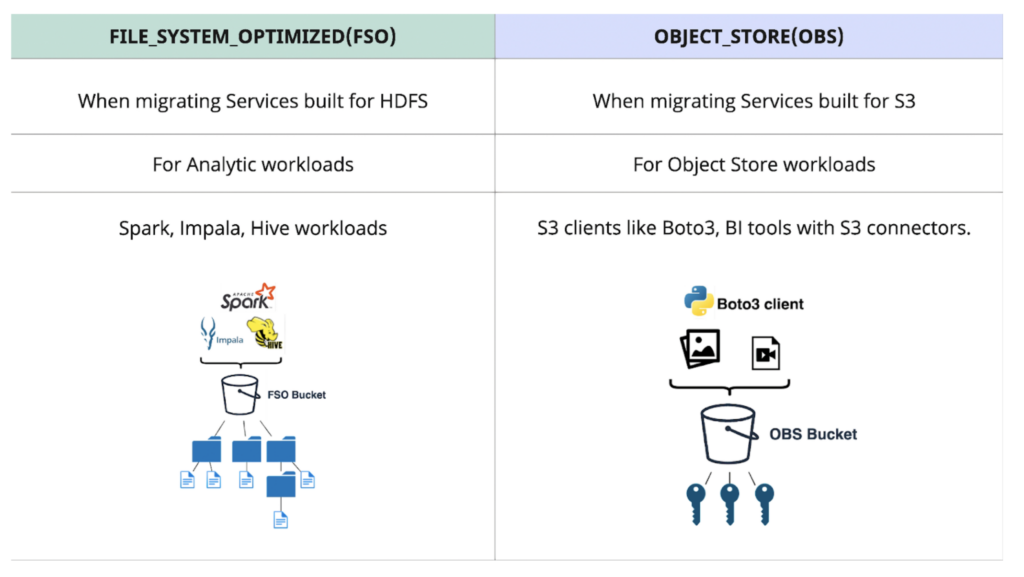 Fig 6. When to use FSO vs OBS
Fig 6. When to use FSO vs OBS
- Analytics services built for HDFS are particularly well suited for FSO buckets:
- Apache Hive and Impala drop table query, recursive directory deletion, and directory moving operations on data in FSO buckets are faster and consistent without any partial results in case of any failure because renames and deletes are atomic and fast.
- Job Committers of Hive, Impala, and Spark often rename their temporary output files to a final output location at the end of the job. Renames are faster for files and directories in FSO buckets.
- Cloud-native applications built for S3 are better suited for OBS buckets:
- OBS buckets provide strict S3 compatibility.
- OBS buckets provide rich storage for media files and other unstructured data enabling exploration of unstructured data.
Summary
Bucket layouts are a powerful feature that allow Apache Ozone to be used as both an Object Store and Hadoop Compatible File System. In this article, we have covered the benefits of each bucket layout and how to choose the best bucket layout for each workload.
If you are interested in learning more about how to use Apache Ozone to power data science, this is a great article. If you want to know more about Cloudera on private cloud, see here.
Our Professional Services, Support and Engineering teams are available to share their knowledge and expertise with you to choose the right bucket layouts for your various data and workload needs and optimize your data architecture. Please reach out to your Cloudera account team or get in touch with us here.
References:
[1] https://blog.cloudera.com/apache-ozone-a-high-performance-object-store-for-cdp-private-cloud/
[2] https://blog.cloudera.com/a-flexible-and-efficient-storage-system-for-diverse-workloads/


