Introduction
Data Lifecycle - collecting data. This tutorial will show you how to use Apache NiFi to pull data from a cloud storage solution, format it to send it into a messaging queue (Kafka), and finally consume from that queue to ingest it into both an Apache Hive ready format and an operational database (HBase).
Prerequisites
- Have access to Cloudera on cloud
- Have created a CDP workload user
- Basic AWS CLI skills
Outline
The video below provides a brief overview of what is covered in this tutorial:
You have two (2) options to get the assets needed for this tutorial:
It contains only necessary files used in this tutorial. Unzip tutorial-files.zip and remember its location.
It provides assets used in this and other tutorials; organized by tutorial title.
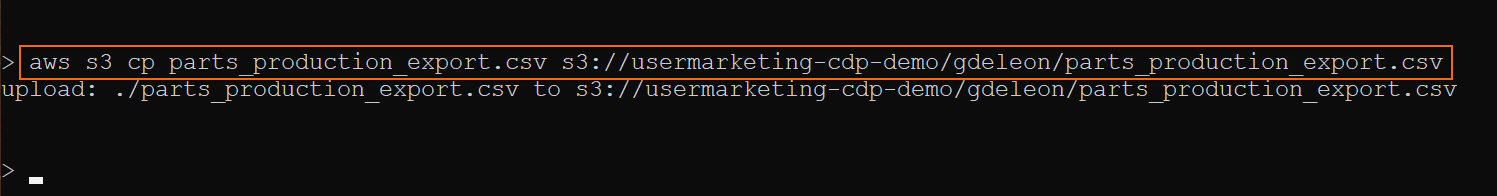
Using AWS CLI, copy file parts_production_export.csv to S3 bucket, defined by your environment’s storage.location.base attribute.
Note: You may need to ask your environment's administrator to get property value for storage.location.base.
For example, property storage.location.base has value s3a://usermarketing-cdp-demo; therefore copy the files using the command:
aws s3 cp parts_production_export.csv s3://usermarketing-cdp-demo/parts_production_export.csv
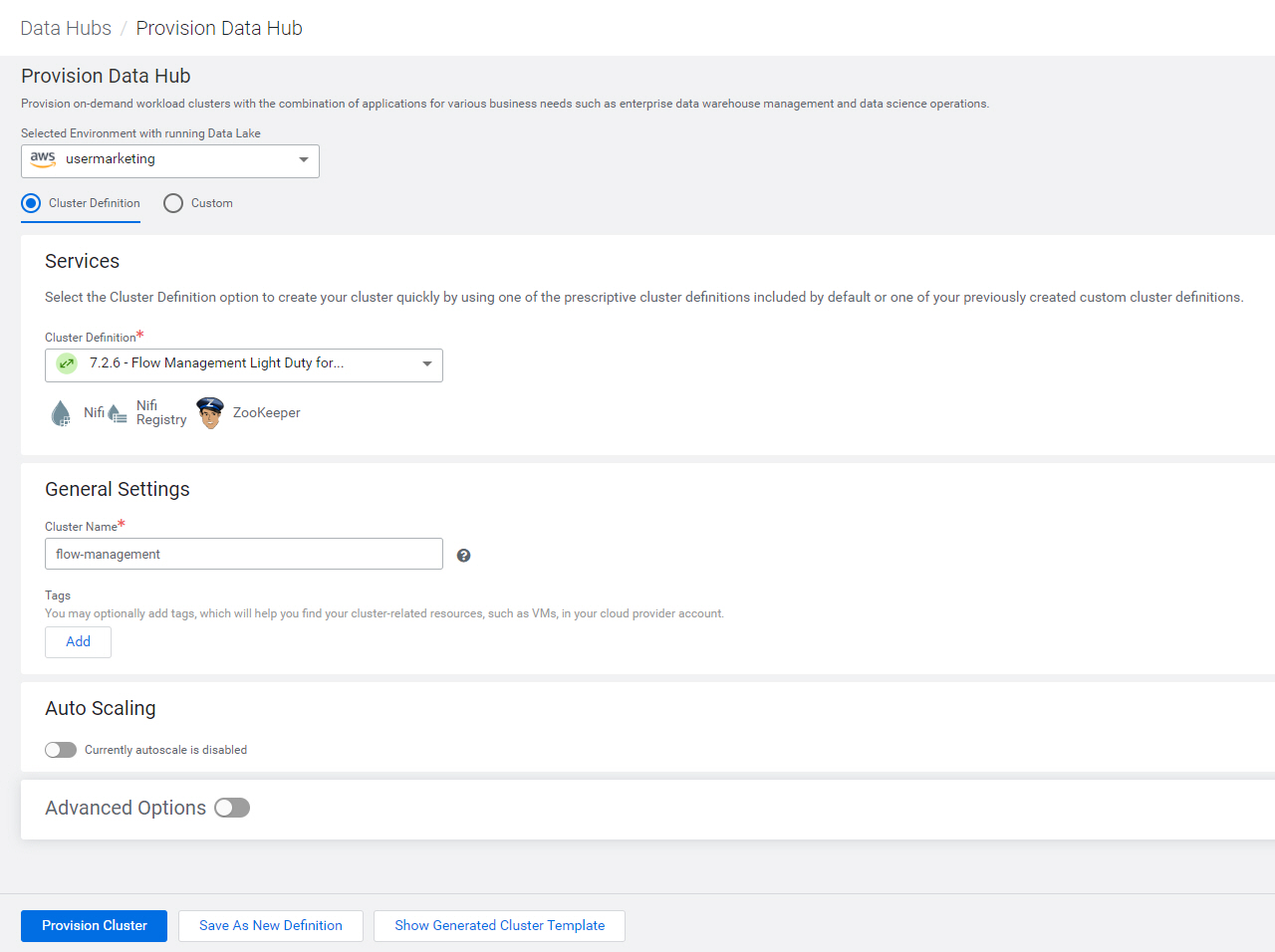
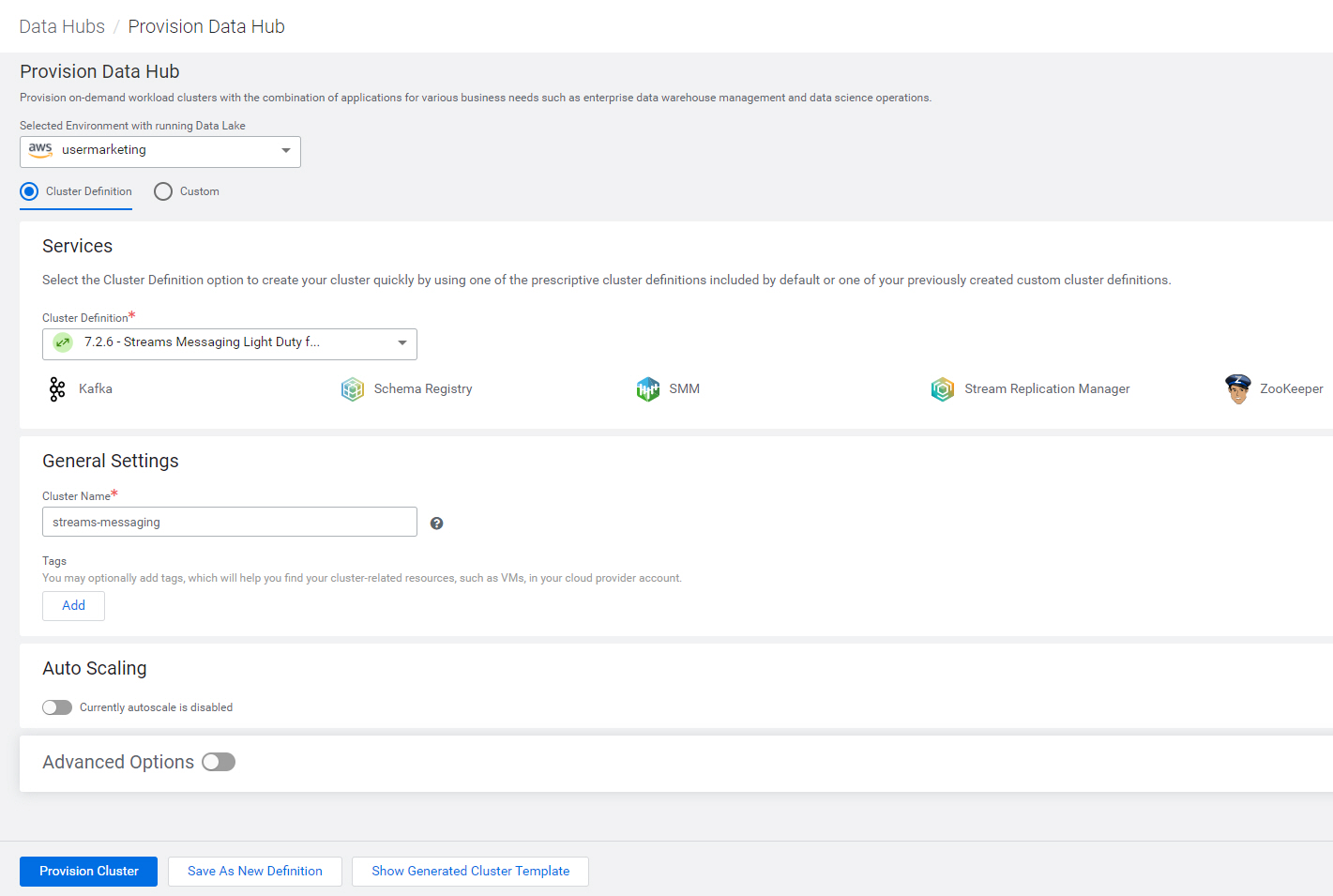
streams-messaging, using cluster definition 7.x - Streams Messaging Light Duty for AWS
operational-database, using cluster definition 7.x - Operational Database with SQL for AWS
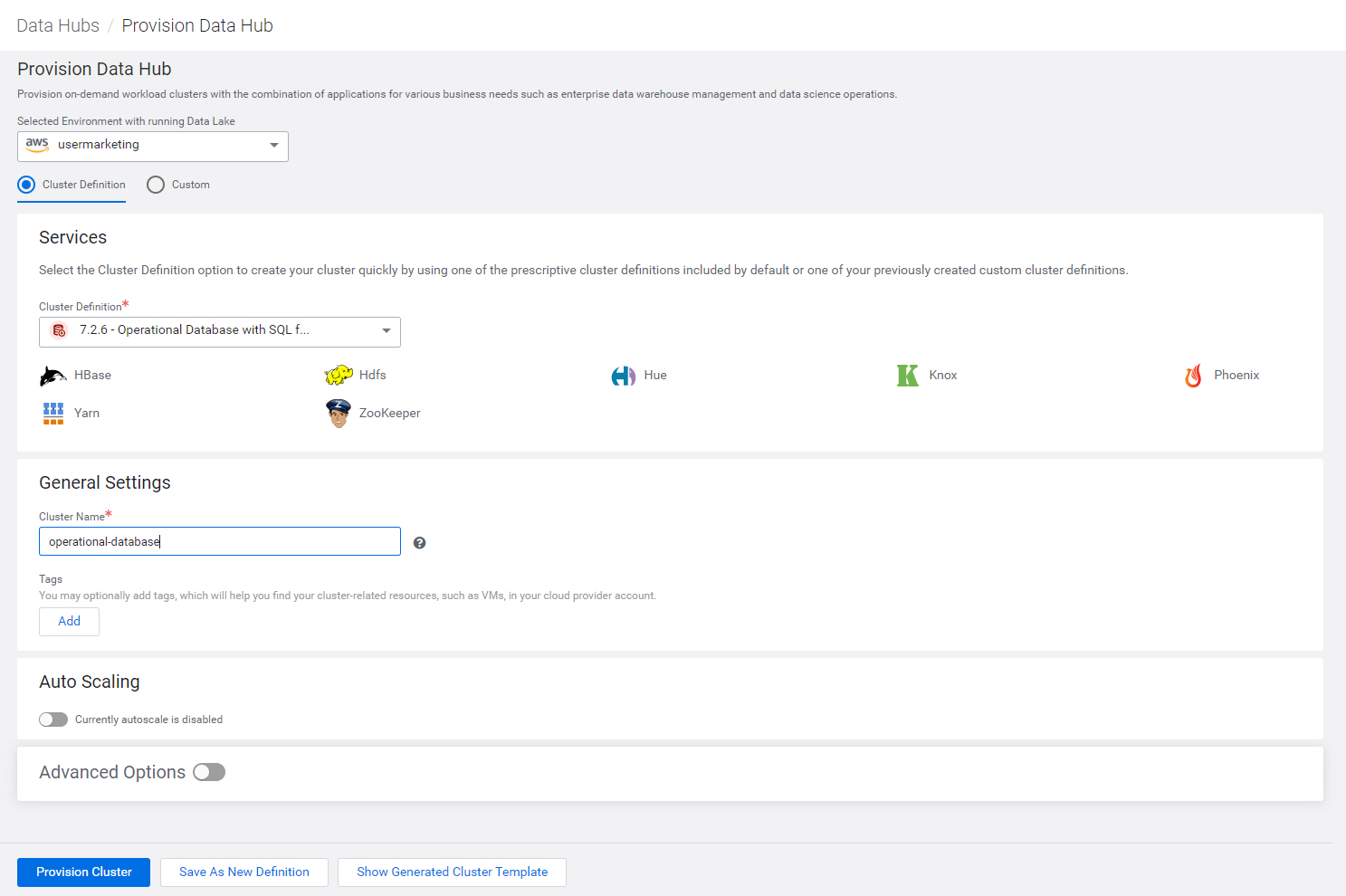
Note: Your CDP environment may have different cluster definitions.
Refer to How to Create a Data Hub on Cloudera for details on how to provision a Data Hub.
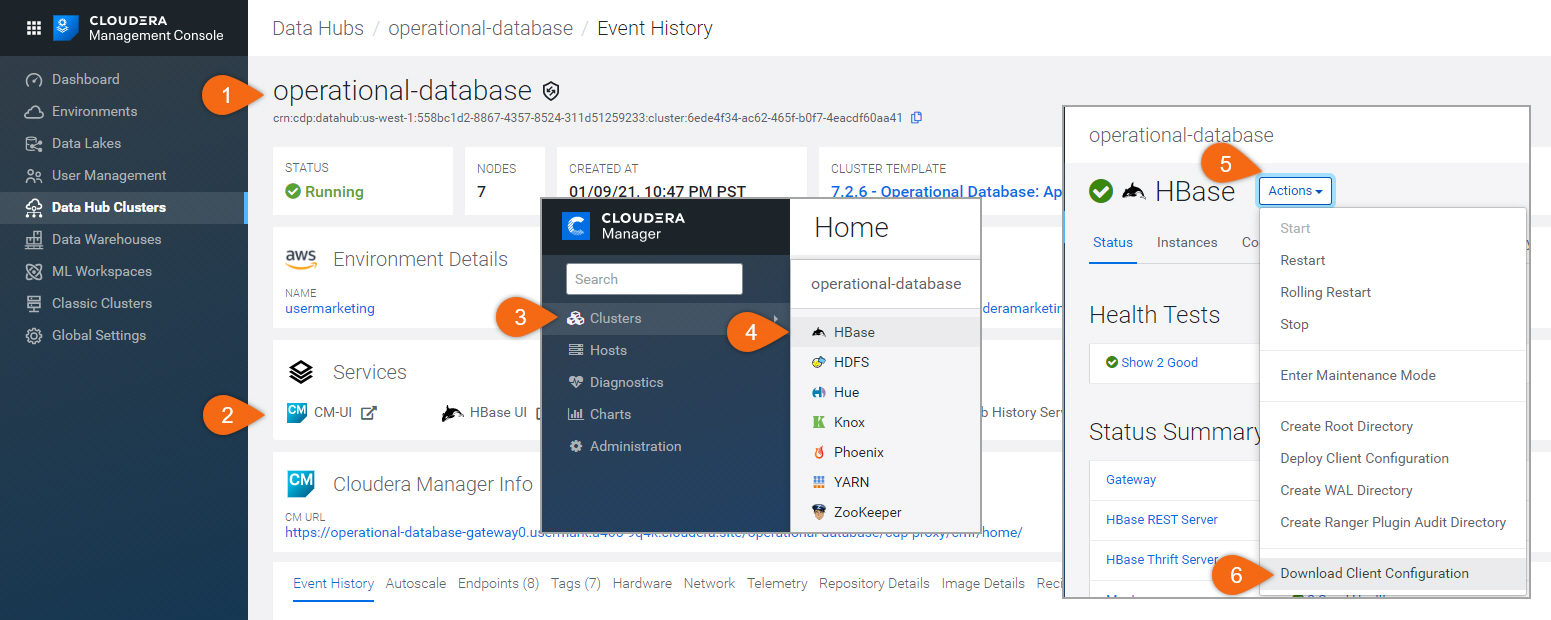
Copy hbase-site.xml file into every NiFi worker node.
Note: There are other files in the client configuration file downloaded - we only need to copy hbase-site.xml.
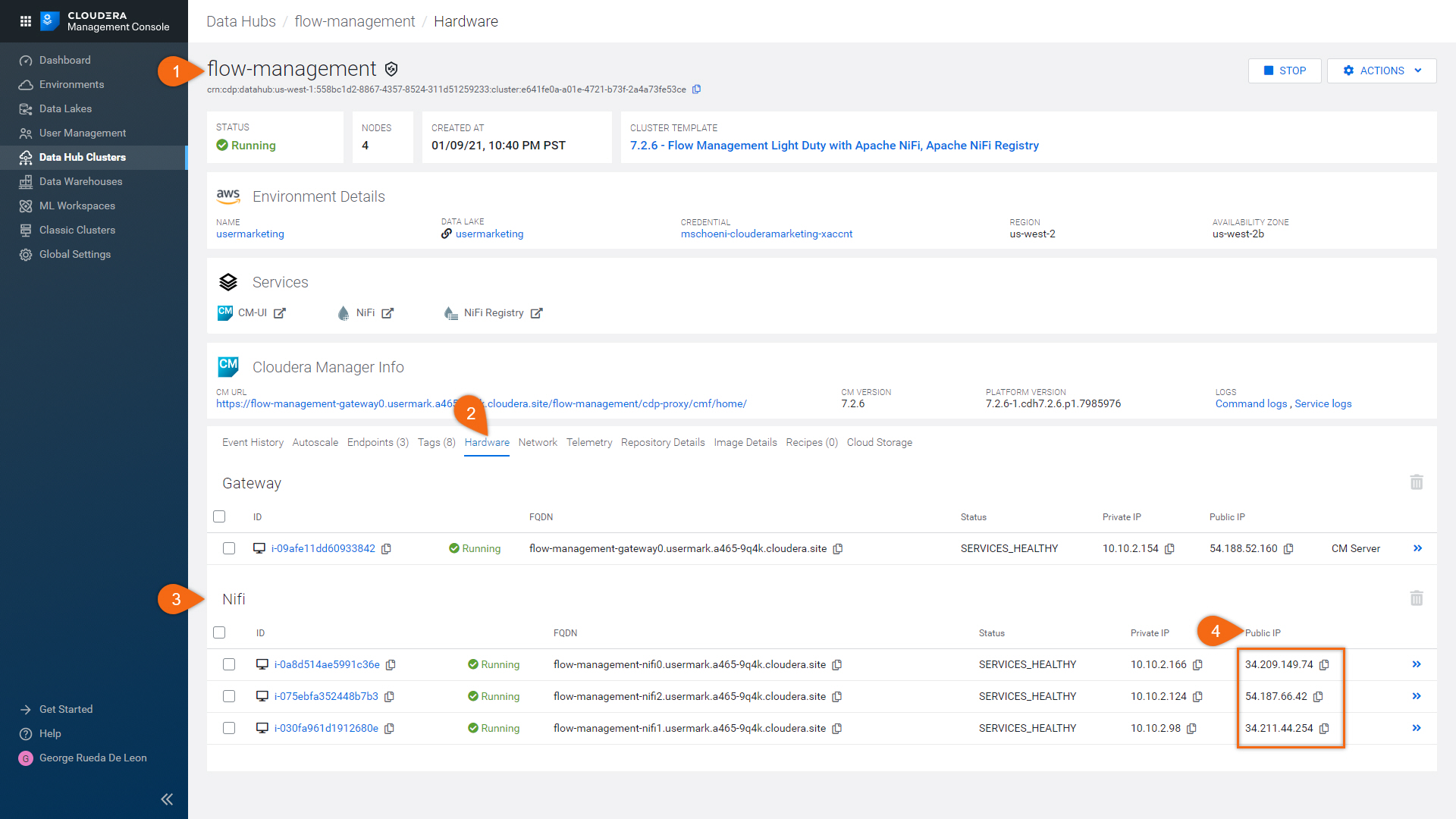
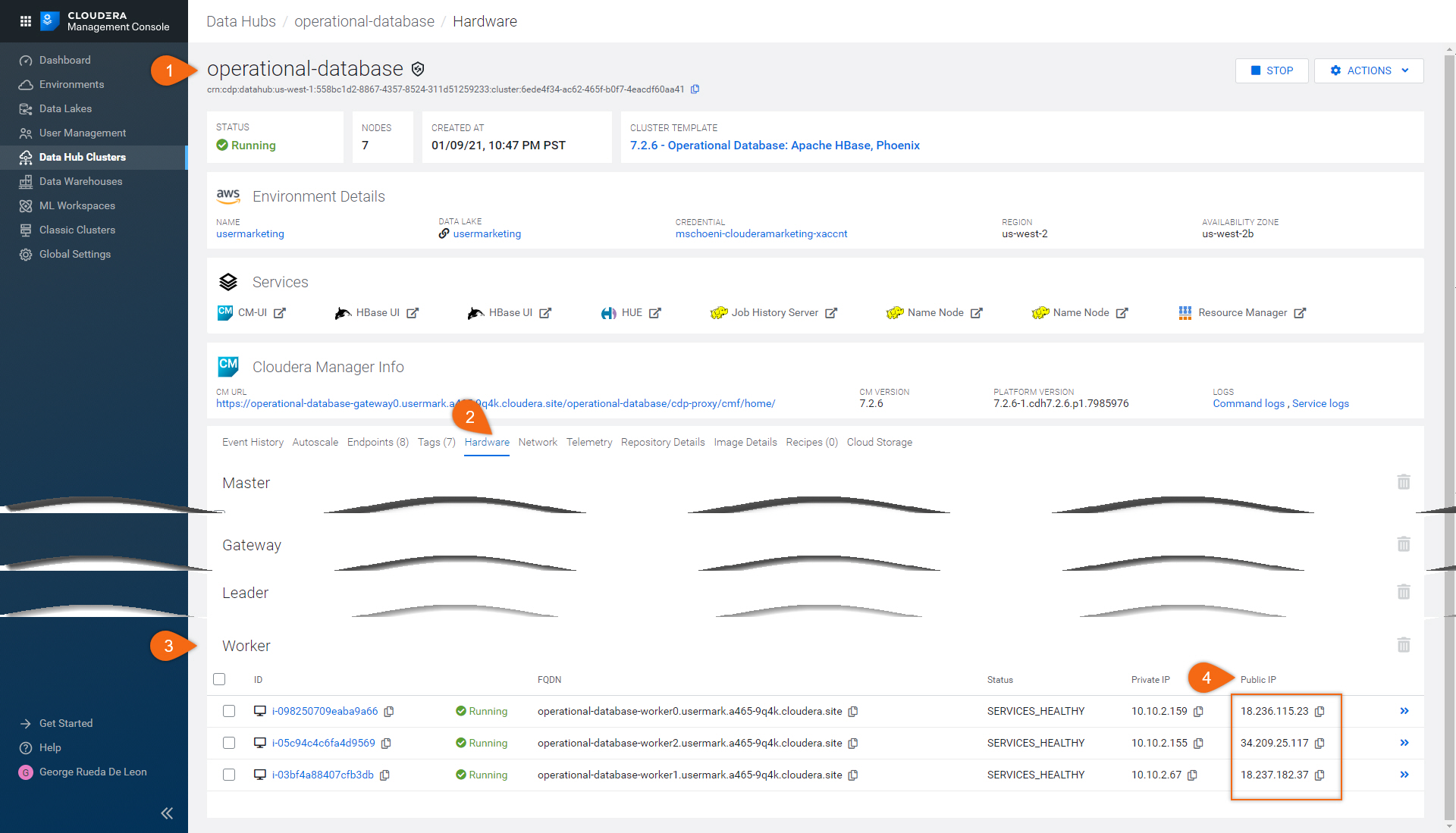
Here is how to find all NiFi worker node(s) public IP addresses:
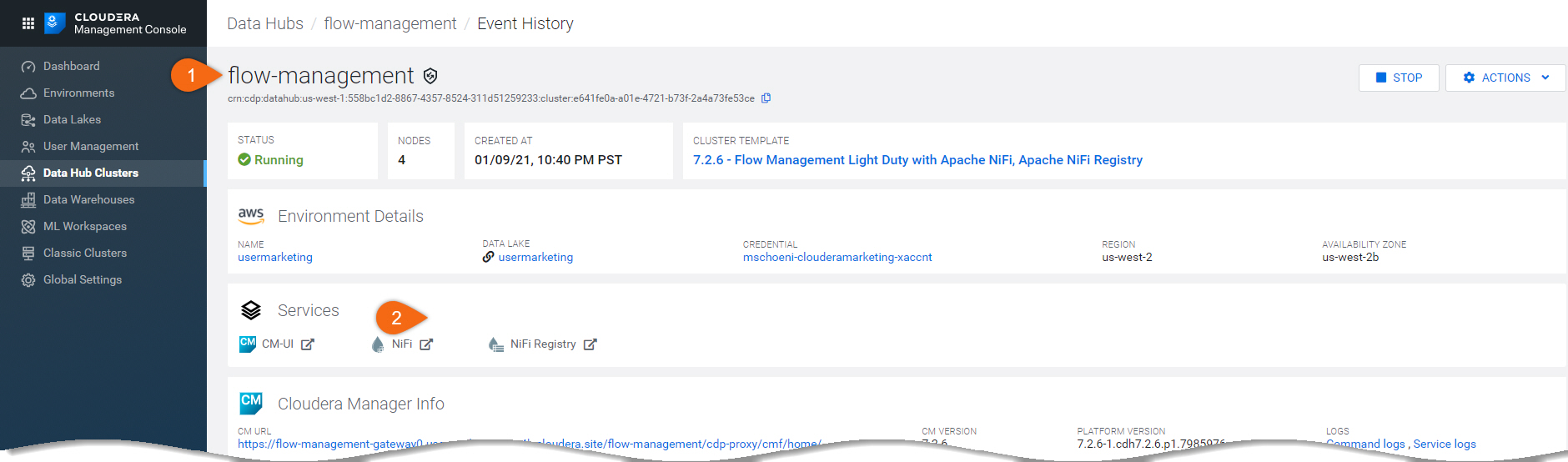
Begin from Flow Management Data Hub:
flow-management > Hardware > NiFi > Public IP
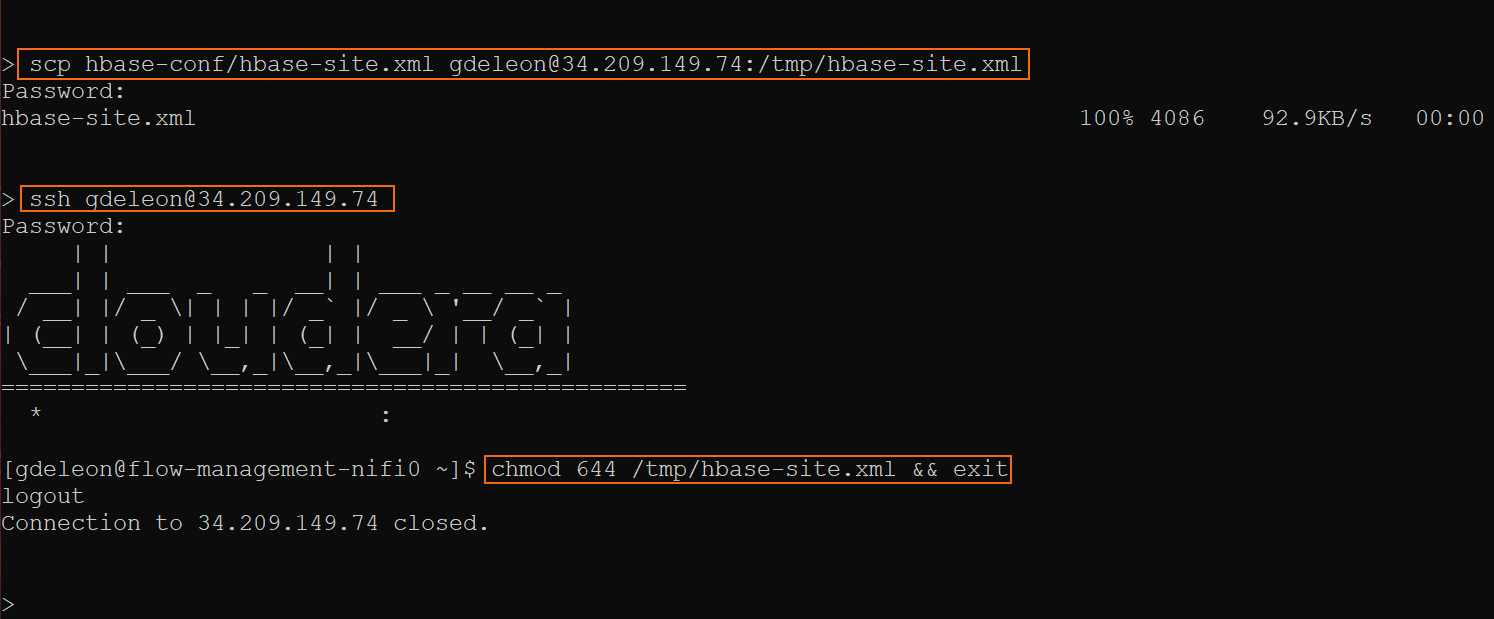
On the command line, issue the following commands on every NiFi worker node. This will copy the HBase configuration file, hbase-site.xml and set permissions accordingly:
Note: You need to update <USERNAME> and <PUBLIC_IP>, where <PUBLIC_IP> is the public IP address of each NiFi worker node.
scp hbase-conf/hbase-site.xml <USERNAME>@<PUBLIC_IP>:/tmp/hbase-site.xml
ssh <USERNAME>@<PUBLIC_IP>
chmod 644 /tmp/hbase-site.xml && exit
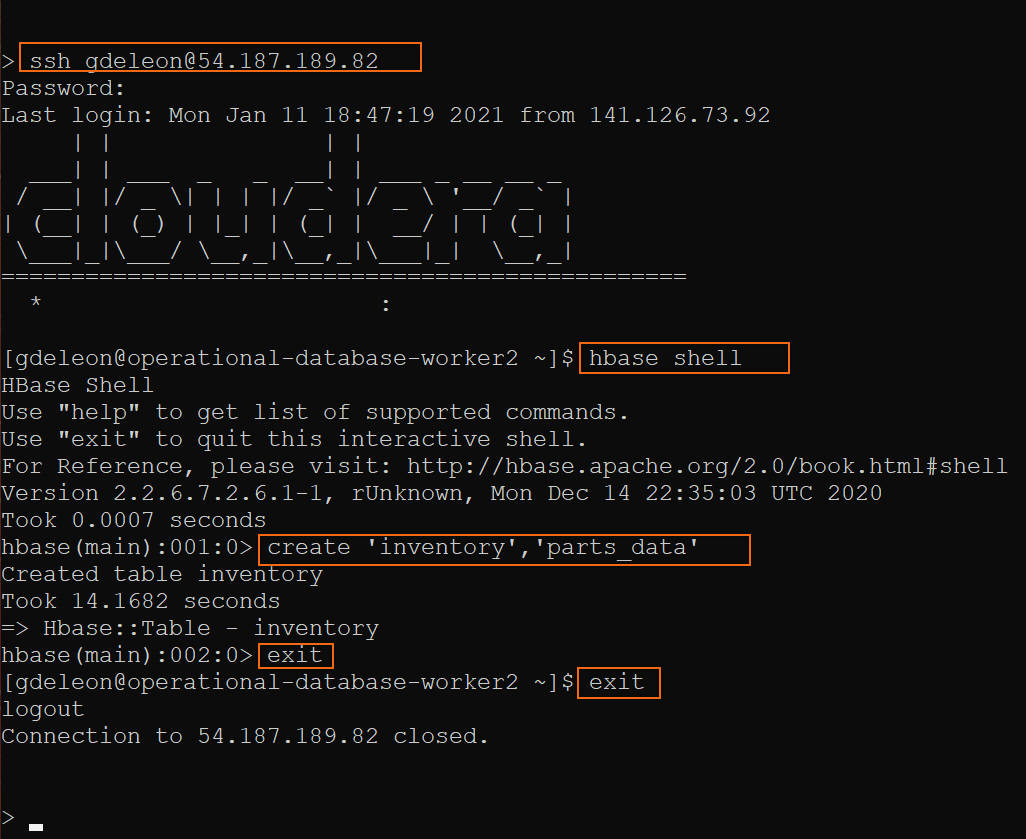
On the command line, SSH into any (one) HBase worker node and issue the following commands to create a table and column family:
Note: You need to update <USERNAME> and <PUBLIC_IP>, where <PUBLIC_IP> is the public IP address of any (one) HBase worker node.
ssh <USERNAME>@<PUBLIC_IP>
hbase shell
create 'inventory','parts_data'
exit
exit
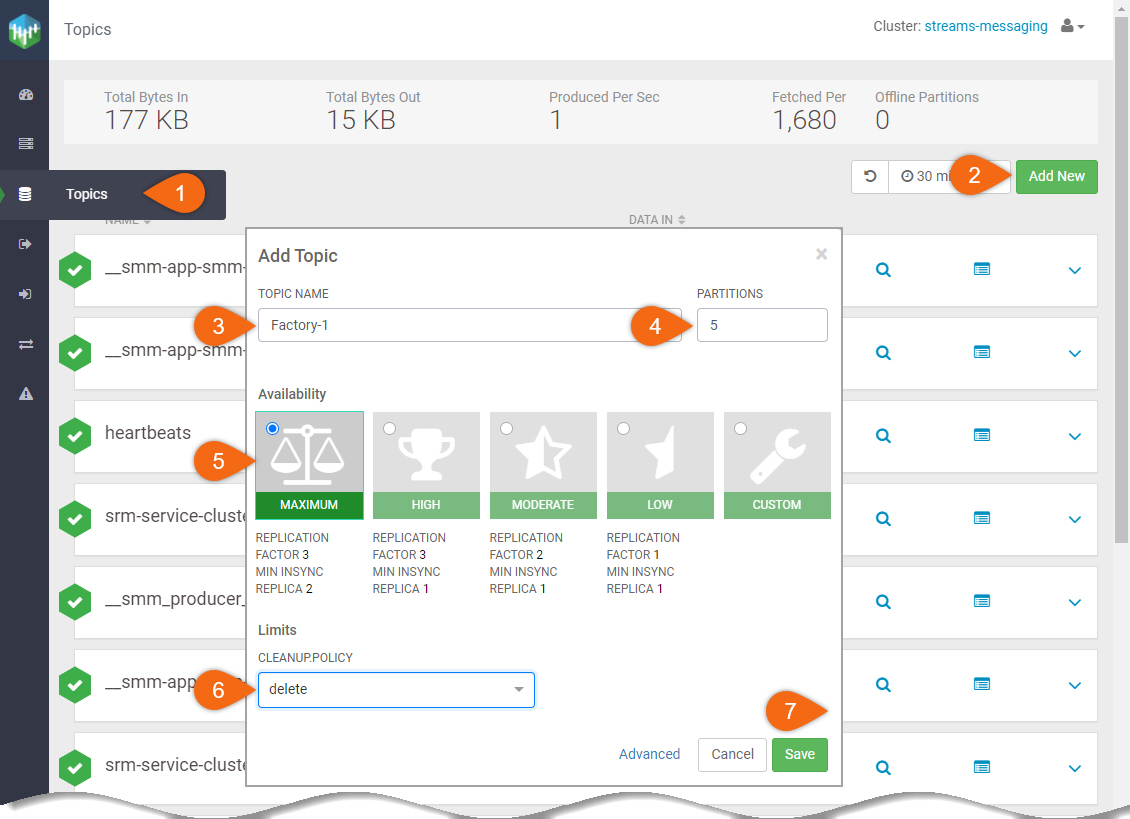
- Select Topics
- Select Add New
- TOPIC NAME:
Factory-1 - PARTITIONS:
5 - Availability: Maximum
- Cleanup Policy: delete
- Save
Repeat the same steps to create the following named topics:
Factory-2
Factory-3
Factory-4
Factory-5
Build and configure NiFi data flow
Instead of building the data flow from scratch, we will use the template provided in download assets. If you want to learn to build the data flow from scratch, take a look at Importing RDBMS Data into Hive.
Begin from Flow Management Data Hub:
flow-management > NiFi
Upload NiFi template
NiFi data flow template, collect-dataflow-template.xml, was provided in download assets. Follow these easy steps to upload.
- Click on
 to upload collect-dataflow-template.xml template
to upload collect-dataflow-template.xml template - Click and drag
 into the canvas and select collect-dataflow-template
into the canvas and select collect-dataflow-template
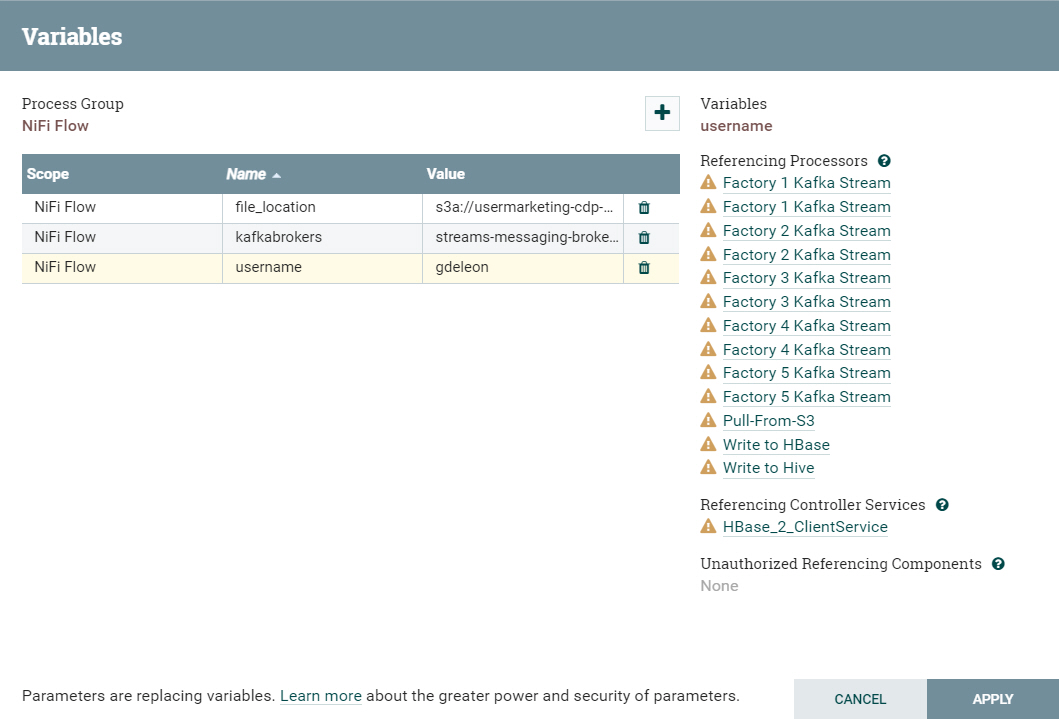
Create variables used in DataFlow
Right-click anywhere on the canvas, outside the processor groups and select Variables.
Click on ![]() to create a new variable:
to create a new variable:
- Name:
username, Value: <use your CDP workload username> - Name:
file_location, Value: <environment’s storage.location.base attribute> - Name:
kafkabrokers, Value: <list of all Kafka broker addresses, separated by commas>
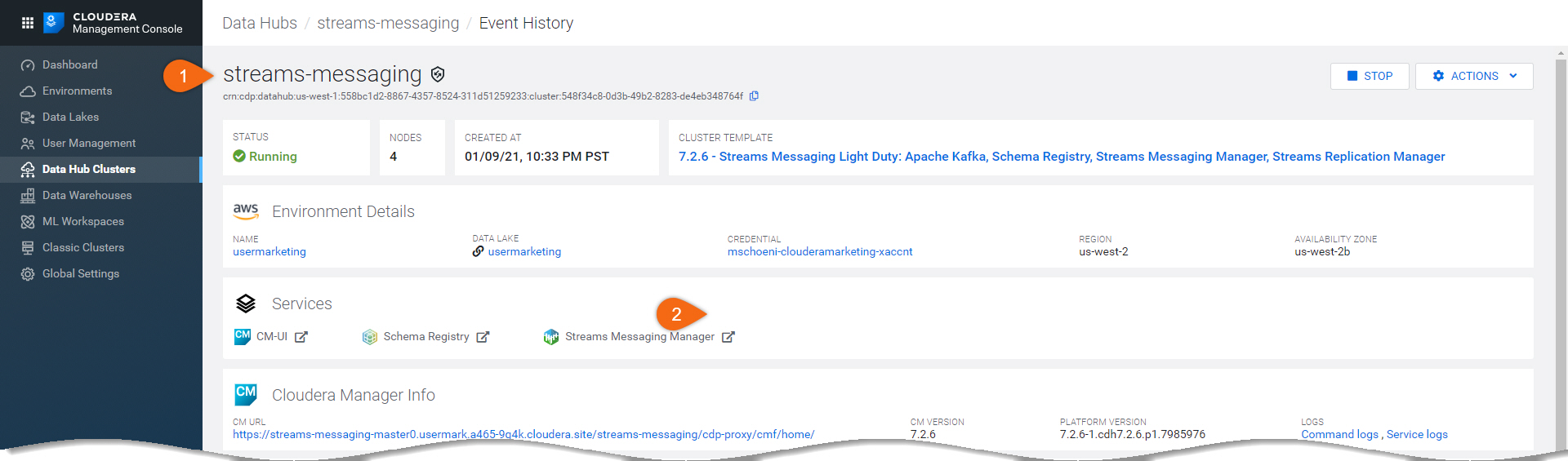
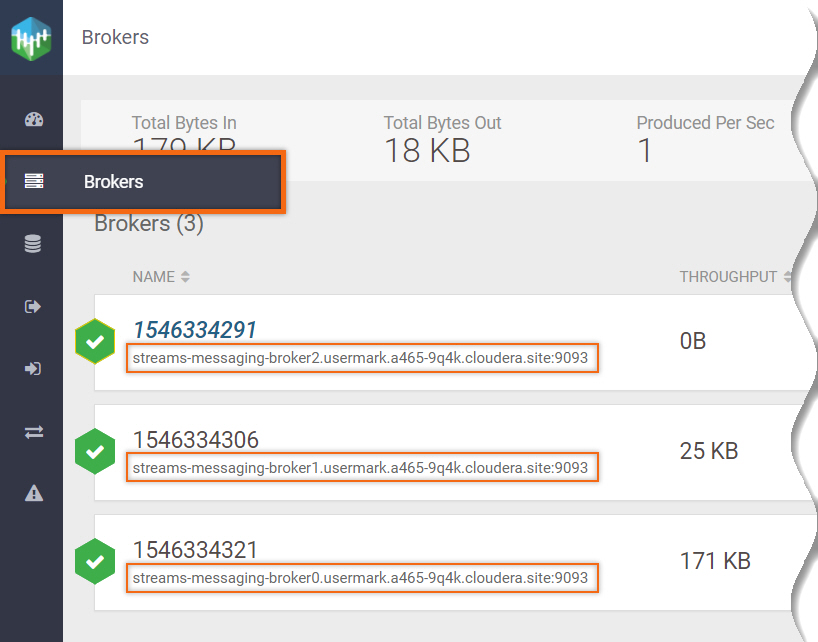
Kafka broker addresses are found in Streams Messaging Data Hub.
streams-messaging > Streams Messaging Manager

Select Brokers
The broker address is located underneath its name.
The variables defined should look something like:
Configure controller services
- Right-click on processor group Push to Kafka
- Select Configure
- Enable CSVReader and CSVRecordSetWriter by clicking on
Note1: You should see two (2) services named Default NiFi SSL Context Service. Delete the one marked with ![]() .
.
- Right-click on processor group Kafka Ingest
- Select Configure
- Enable CSVReader and both CSVRecordSetWriter by clicking on
Note2: Do not close Kafka Ingest configuration window after enabling the service controllers. We have one (1) more controller to enable.
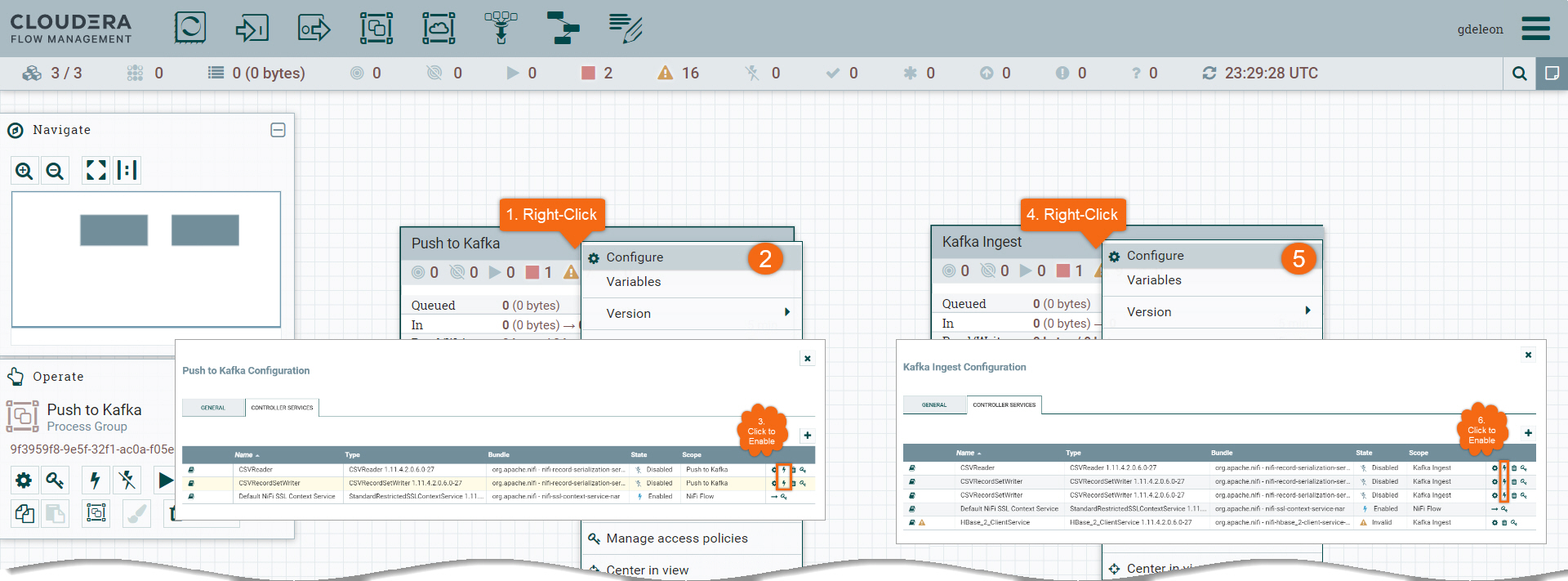
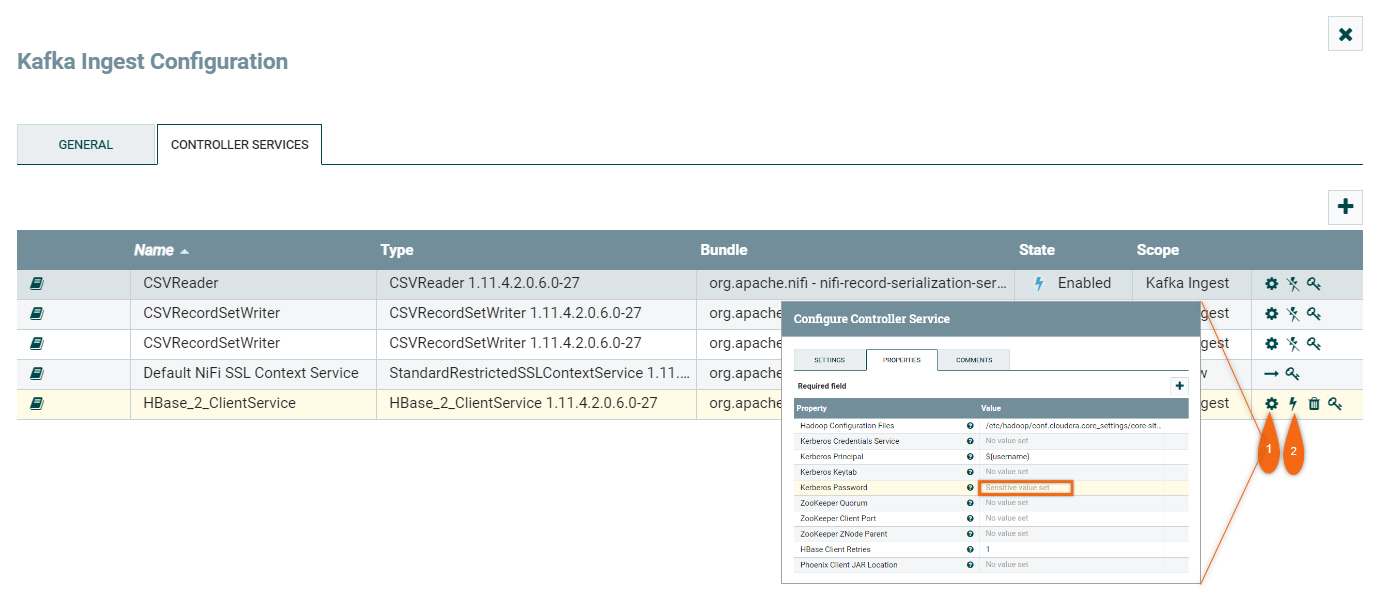
There are two (2) steps in enabling HBase_2_ClientService controller:
- Update property Kerberos Password with your CDP workload password by clicking

- Enable it by clicking
Configure processors
Several processors, in each group, require passwords. We will update them using your CDP workload password.
Push to Kafka processor group
Expand processor group and update properties for the following processors:
- Pull-From-S3: update Kerberos Password
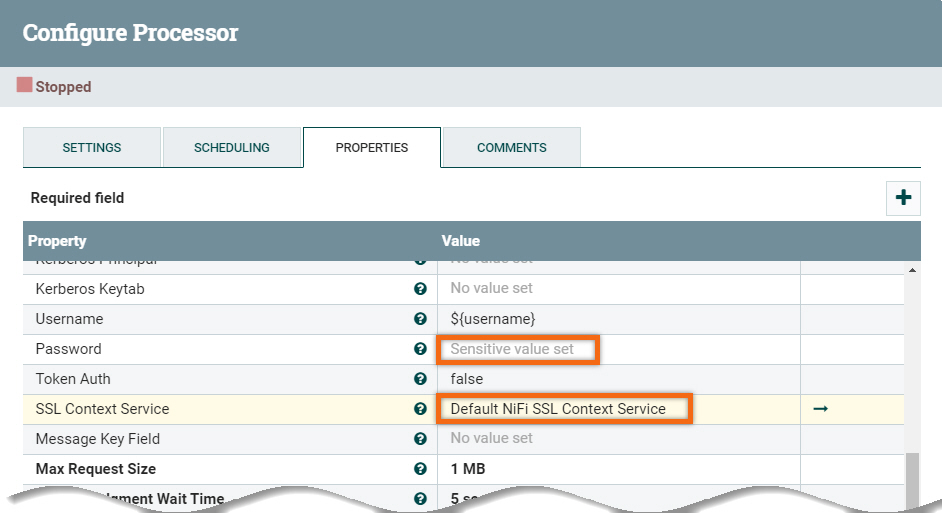
- Factory 1 Kafka Stream: update Password and SSL Context Service with Default NiFi SSL Context Service
- Factory 2 Kafka Stream: update Password and SSL Context Service with Default NiFi SSL Context Service
- Factory 3 Kafka Stream: update Password and SSL Context Service with Default NiFi SSL Context Service
- Factory 4 Kafka Stream: update Password and SSL Context Service with Default NiFi SSL Context Service
- Factory 5 Kafka Stream: update Password and SSL Context Service with Default NiFi SSL Context Service
Kafka Ingest processor group
Expand processor group and update properties for the following processors:
- Factory 1 Kafka Stream: update Password and SSL Context Service with Default NiFi SSL Context Service
- Factory 2 Kafka Stream: update Password and SSL Context Service with Default NiFi SSL Context Service
- Factory 3 Kafka Stream: update Password and SSL Context Service with Default NiFi SSL Context Service
- Factory 4 Kafka Stream: update Password and SSL Context Service with Default NiFi SSL Context Service
- Factory 5 Kafka Stream: update Password and SSL Context Service with Default NiFi SSL Context Service
- Write to Hive: update Kerberos Password
Run Data Flow
Let's run the data flow you have just created. You have the option to run all processor groups, a processor group at a time or single processor at a time. For general debugging and diagnostics, it is recommended to run one processor at a time. This will allow you to validate data in the list queues.
We will run one processor group at a time.
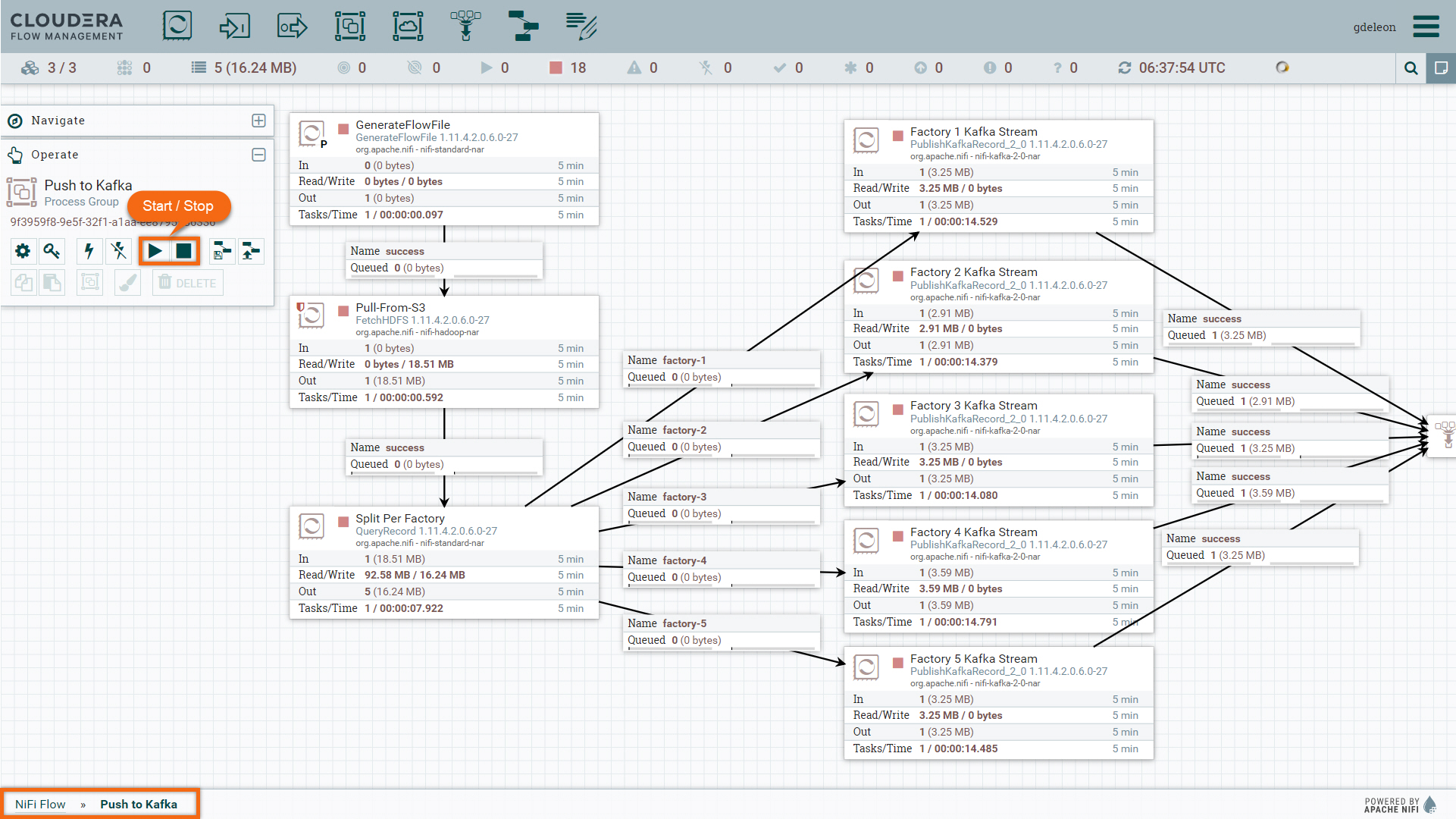
Expand processor group Push to Kafka and run all processors at once by clicking ![]() in the Operate menu.
in the Operate menu.
After a few seconds, you will see the data flow through all the processors. Click on ![]() from the Operate menu to stop all processors at once.
from the Operate menu to stop all processors at once.
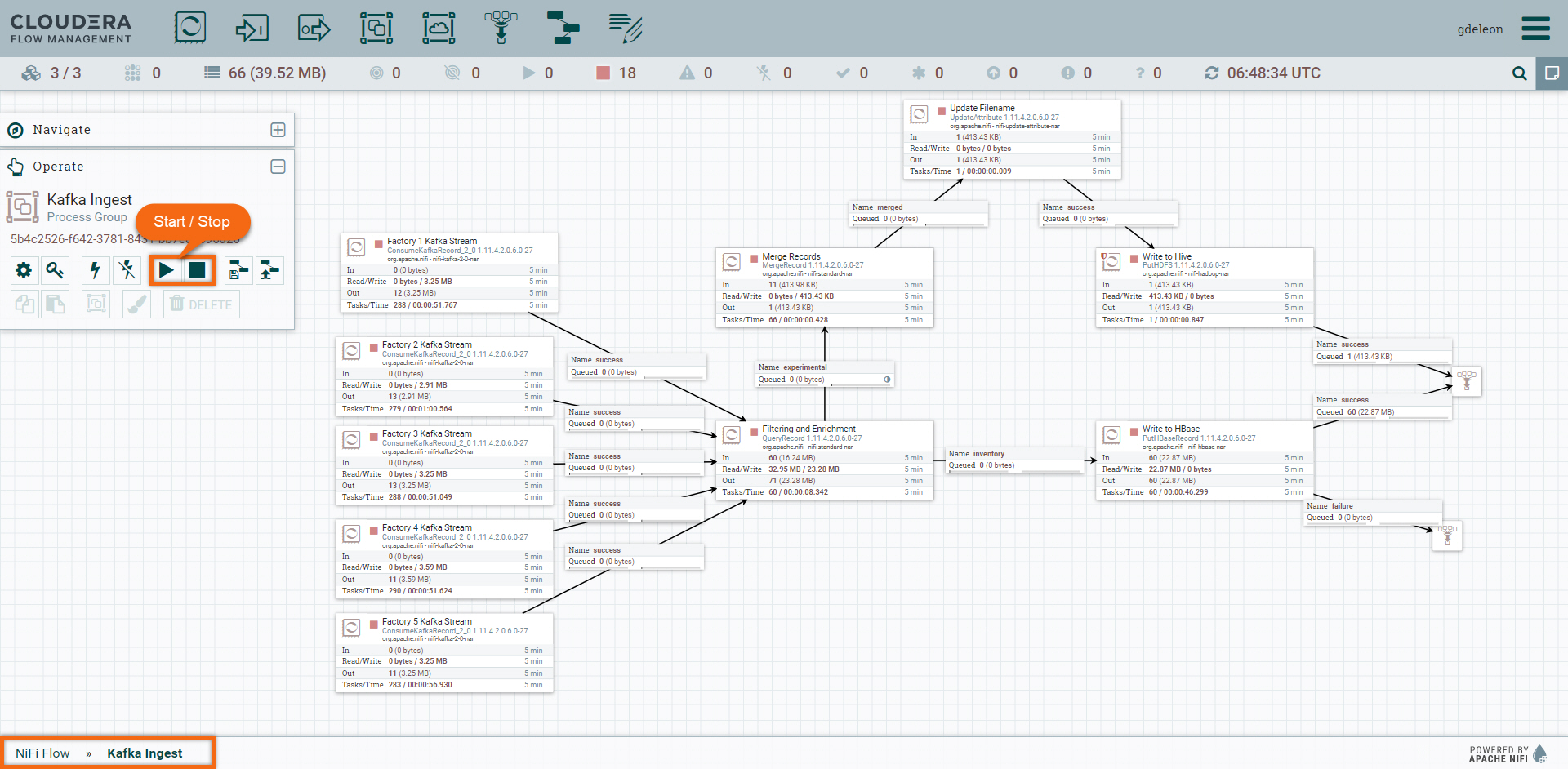
Expand processor group Kafka Ingest and run all processors at once by clicking ![]() in the Operate menu.
in the Operate menu.
After a few seconds, you will see the data flow through all the processors. Click on ![]() from the Operate menu to stop all processors at once.
from the Operate menu to stop all processors at once.
Let’s see metrics on one of the Factory Kafka Topics we created.
Begin from Streams Messaging Data Hub:
streams-messaging > Streams Messaging Manager

Let's take a look at one of the factory's profile.
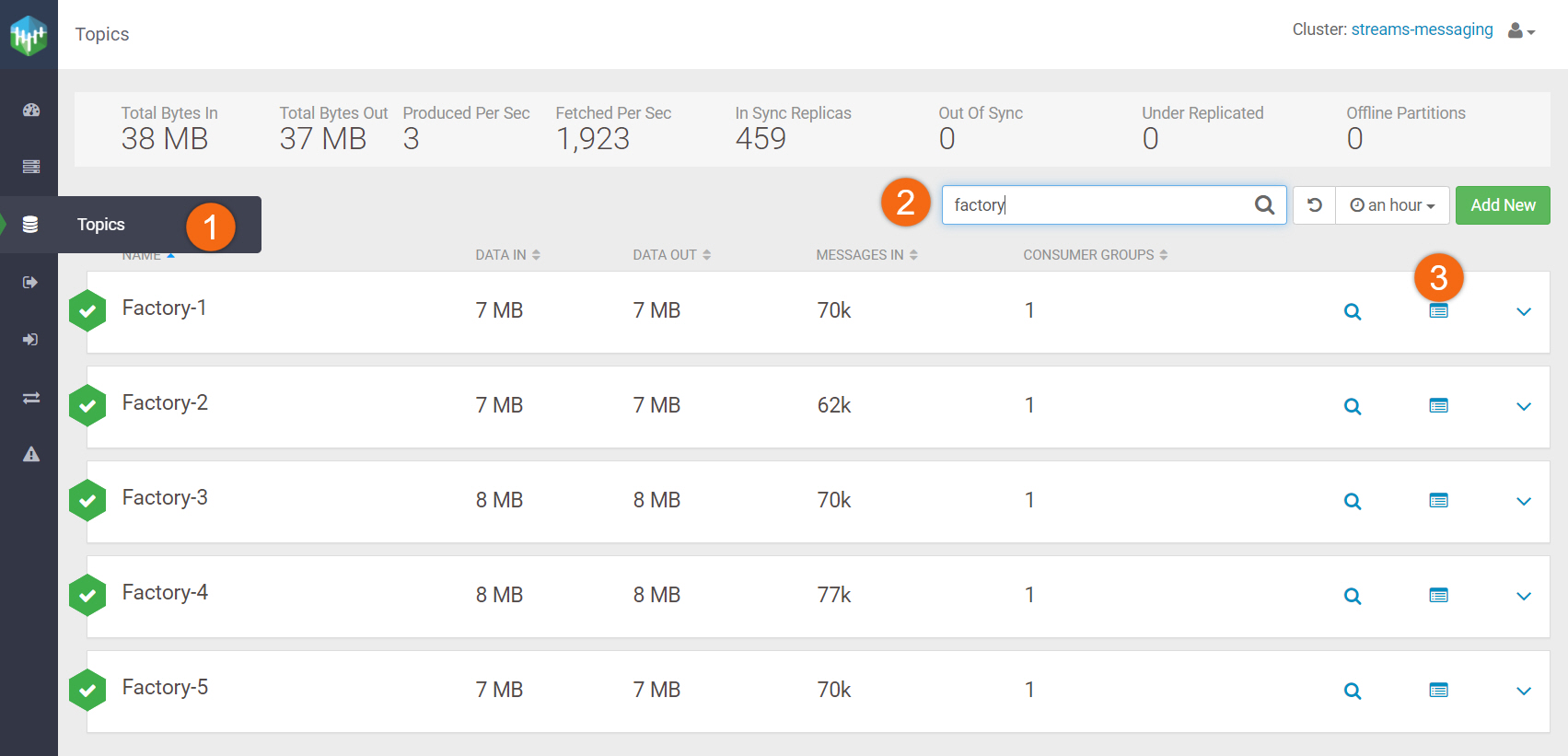
- Select Topics
- Search for factory
- Click on
 to view profile for Factory-1.
to view profile for Factory-1.
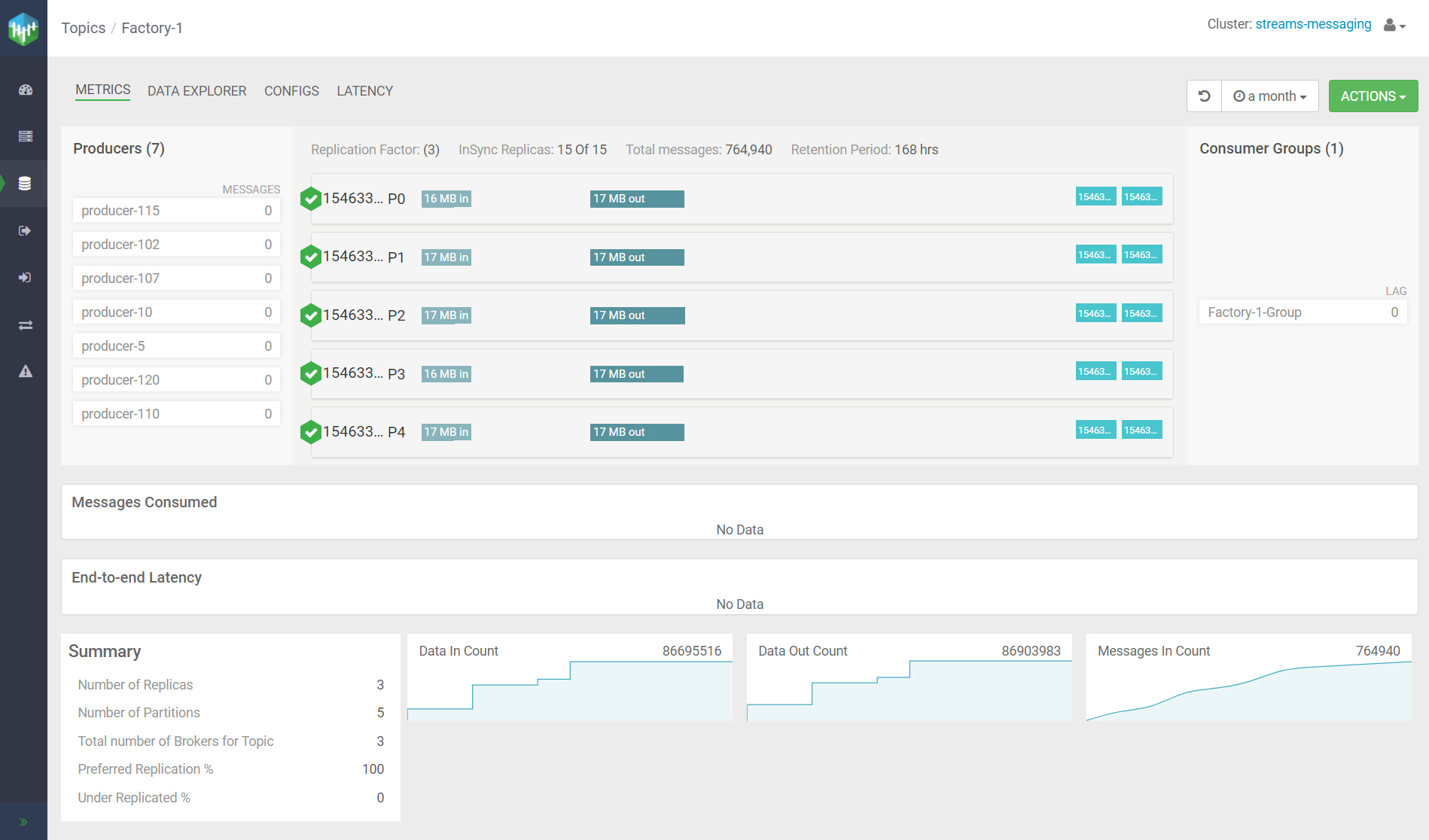
Here's an example of metrics gathered for Factory-1:
View HBase Data
Let's take a brief look at the data stored in HBase table inventory:
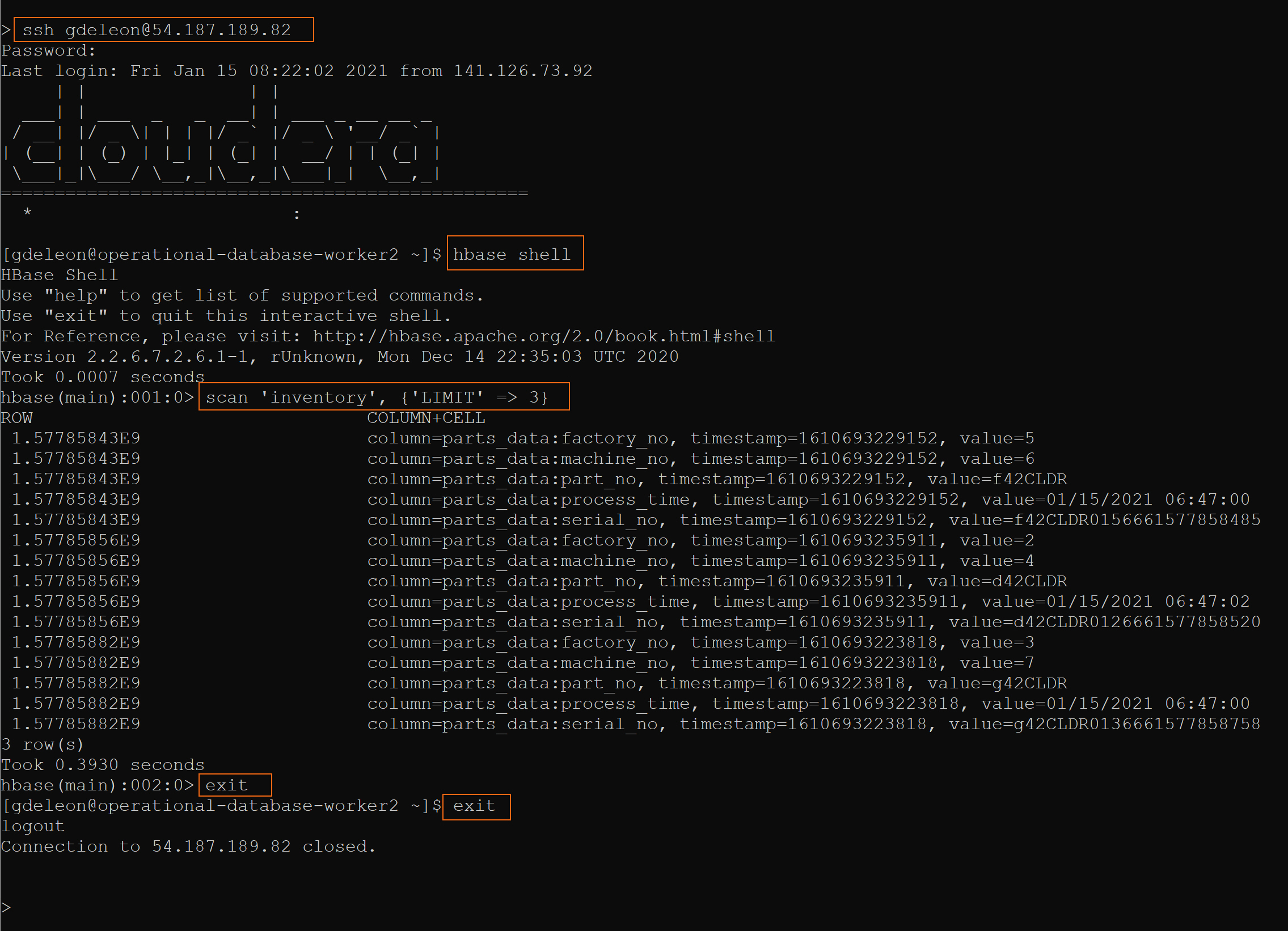
On the command line, SSH into any (one) HBase worker node and issue commands - just as you did before:
Note: You need to update <USERNAME> and <PUBLIC_IP>, where <PUBLIC_IP> is the public IP address of any (one) HBase worker node.
ssh <USERNAME>@<PUBLIC_IP>
hbase shell
scan 'inventory', {'LIMIT' => 3}
exit
exit
Summary
Congratulations on completing the tutorial.
As you've now experienced, it takes a small amount of effort to configure multiple Data Hub clusters to communicate with one another using Cloudera on cloud.
NiFi’s flexible processors make it simple to extract, transform and load data into HBase - hopefully this tutorial sparks your imagination and inspires other creative solutions.
Tutorials
Other
- Have a question? Join Cloudera Community
- Cloudera Data Hub documentation
- Cloudera Operational Database product information