Overview
This five-day course provides the in-depth explanation and skills to become highly productive with Kubernetes by teaching its architecture, deployment, configuration, logging, reporting, and more. Kubernetes's complexity is due to its extensive feature set and intricate object model, which includes concepts like Pods, Deployments, and Services. It also relies on YAML configuration files and requires managing a distributed system across multiple nodes. The course provides references for architecture and recommended practices used by administrators.
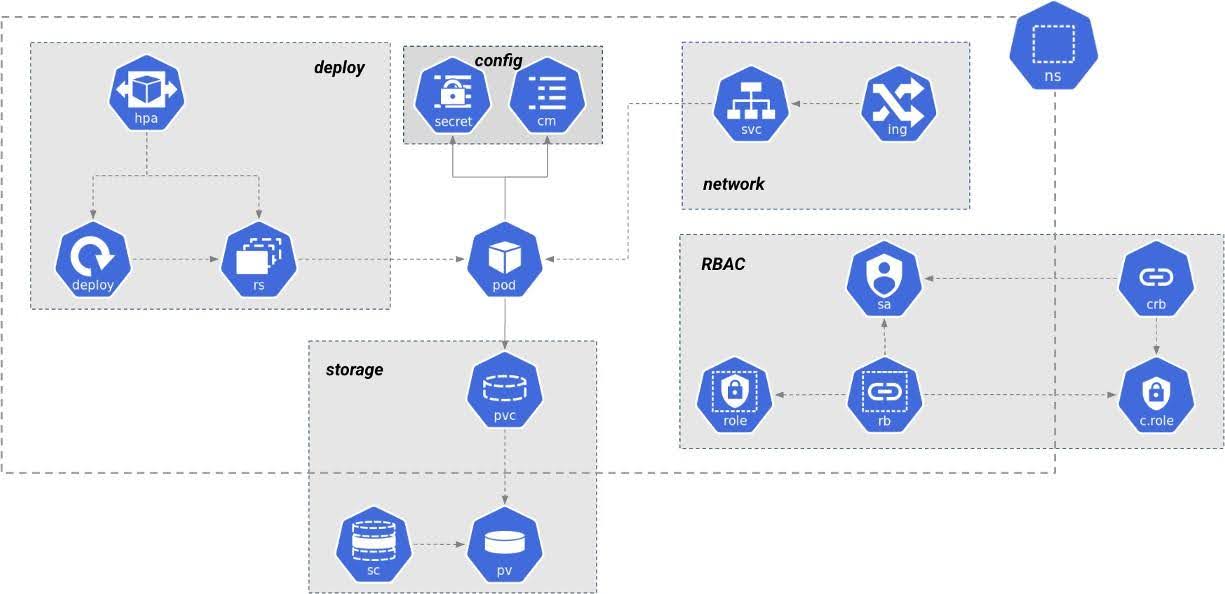
What you'll learn
- Understand the architecture of Kubernetes and its components.
- Deploy and manage applications on Kubernetes.
- Utilize Kubernetes features for scaling and self-healing.
- Implement best practices for security and networking.
- Troubleshoot common issues in Kubernetes environment
Who Should Take This Course?
This course is an immersive training for a full range of Kubernetes users, from administrators to DevOps to developers. This course is intended for senior technicians with strong skills in Linux and application lifecycle. Students must have proficiency in Linux CLI. Students must have access to high-speed Internet to download various public Git repositories. The classroom environment is a four-node cluster running on Linux.
Book the course
Course Details
Get Aboard
- Introduction to Visual Studio Code
- Introduction to Git repos
- Documentation and Resources
Access and Interact
- Building Kubernetes Clusters
- Implementing Container Network Interface
- Install kubectl and K9s
Architecture
- Kubernetes Design Principles
- Kubernetes Clusters
- Kubernetes Control Plane
- Kubernetes Networking
Microservices
- The purpose of microservices
- Running Docker containers
- Building a microservice
Running Kubernetes
- Manifest Files
- Namespaces
- Pods
- Labels and Selectors
- Pod Logging
- Deployments
- Services
- Multi-Container Pods
- Init Containers
User Authentication
- User Authentication
- Controller Manager User Certificates
- Manage CertificateSigningRequests
- Manage User Certificates
- Submitting with curl
- Static Files for Passwords or Tokens
User Access Control
- Architecture for Authorization
- Authorization Modes
- CLI Process
- Manifest Files
Cluster Role Access Control
- Cluster Roles
- Cluster Role Binding
- Manifest Files
Service Accounts
- Service Accounts
- Create a Service Account
- Inspect a Service Account
- Default Service Account
- Disable Service Account Token
Kubeconfig
- Kubeconfig and Multicluster Access
- Running Multi-Node Clusters
- User Config Files
- Manage Contexts
Docker Storage
- Docker Storage Architecture
- Storage Drivers
- Volume Drivers
Storage
- Volumes
- Volume Types
- Persistent Volumes
- Persistent Volume Claims
- Storage Classes
- Creating CSI Volumes
Operations
- Rolling Out Versions
- Health Probes
- Performance Testing with K6
- Horizontal Auto Scalers
- Storage Classes
- Creating CSI Volumes
Scheduling Pods
- Scheduling Process
- Manual Scheduling
- Node Labels and Node Selectors
- Node Affinity
- Pod Affinity and Pod Antiaffinity
- Taints and tolerations
Scheduling Resources
- CPU and Memory Units
- Monitoring Tools
- Resource Requests
- Resource Limits
- Managing Resources
- Quality of Service
- Resource Quotas for Namespaces
Command, Args, and Env
- Docker CMD and ENTRYPOINT
- Kubernetes CMD and ARGS
- Environment Variables
Config Map and Secret
- ConfigMaps
- Create ConfigMaps
- Inject ConfigMaps
- Secrets
- Create Secrets
- Inject Secrets
- Private Registry
Networking
- Kubernetes Networks
- OSI Architecture
- Network Architecture
- External Load Balancer
- Host Network
- Service Network
- Pods Network
Cluster DNS
- Domain Name Service
- CoreDNS
- Switch Namespace Context
- Kube-Proxy and iptables
Services
- Services
- Connect to an Endpoint
- Types of Services
- Service ClusterIP
- Service NodePort
- Service LoadBalancer
- Service Commands
Ingress
- Ingress Controllers
- Ingress Resources
- Ingress Routing Rules
- Configure Ingress
Network-Policies
- Network-Policies
- Rules for Network Policies
- Templates for Network Policies
- Create Network Policies
Maintaining
- Static Pods
- Daemonsets
- etcd
- Backups
- Upgrade Control Plane
- Upgrade Workers
- Inspect Clusters
- Fault Isolation Process
Summary
- Next steps
- Cloudera Support

