Enterprise-grade AI for hybrid environments
Cloudera AI supports traditional ML, GenAI, and agentic AI; offers secure, scalable, and governed AI development; and ensures data and model privacy from idea to deployment.
Accelerate generative and agentic AI development with low-code to full-code flexibility.
Deploy any model, anywhere, with enterprise-grade performance and scale.
Ensure governed, compliant, and private AI workflows across the entire AI lifecycle.
Accelerate enterprise AI.
Move from idea to impact faster. Cloudera gives you the tools to build, scale, and secure AI—so your enterprise stays ahead.
-
Fast-track AI innovation
Accelerate AI development with integrated, no-code and full-code tools.
-
Run any model at enterprise scale
Deploy, serve and manage any model across cloud or on premises at scale.
-
Private AI by design
Keep sensitive data and models private with end-to-end governance.
-
Fast-track AI innovation
Accelerate AI development with integrated, no-code and full-code tools.
-
Run any model at enterprise scale
Deploy, serve and manage any model across cloud or on premises at scale.
-
Private AI by design
Keep sensitive data and models private with end-to-end governance.
Build and launch AI projects quickly.
Move from concept to MVP in days with no-code AI Studios, AI Assistants, and AMPs.
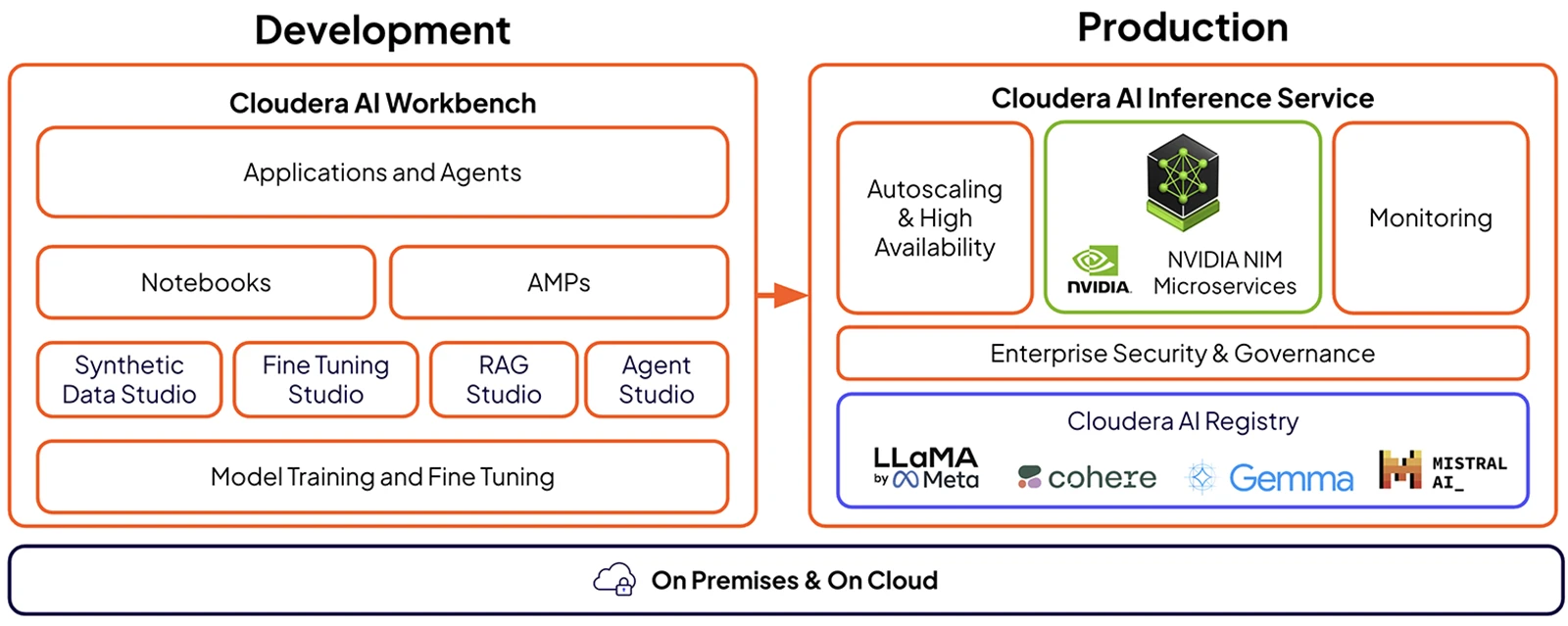
The Cloudera AI Inference service delivers autoscaling, monitoring, and reliability.
Serve traditional and GenAI models securely, with built-in governance, for enterprise AI production workloads.
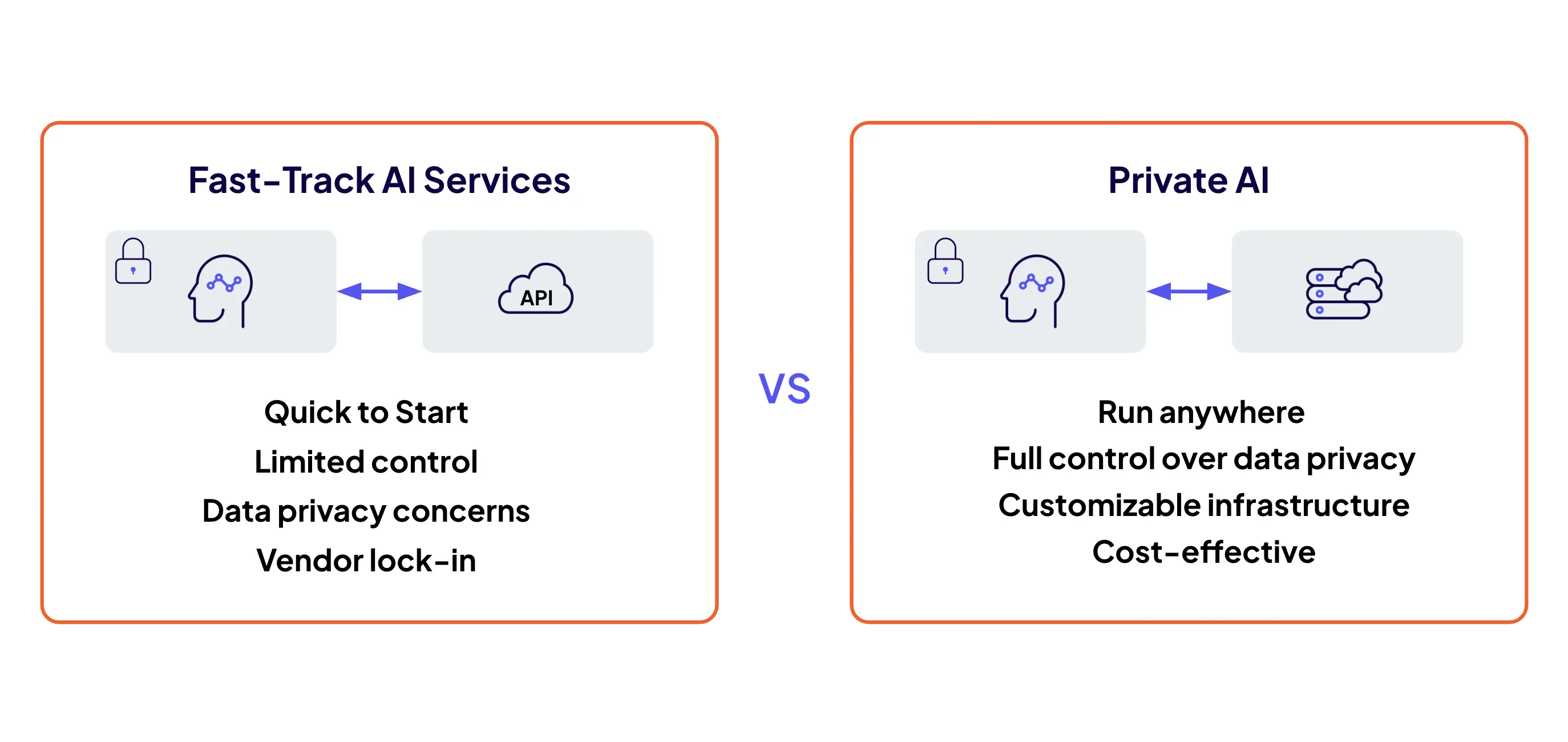
Protect data, prompts, and models—governed, compliant, and in your environment.
Enforce unified policy, security, and lifecycle control across your AI stack, ensuring open-source flexibility.
Rapidly build AI applications and agents with secure, governed access to data and compute. Seamless support for data exploration and data science, model training, fine-tuning, and integration with local editors or hosted notebooks.
Simplify GenAI application and agent development, giving enterprises an easier, faster path to production while maintaining security, governance, and scalability.
Ready-to-deploy, production-grade reference solutions for common ML and AI use cases that can be easily adapted to your unique requirements to reduce time to value.
Embedded GenAI tools that enhance productivity and accelerate insights across your data and AI lifecycle.
Easily deploy and manage AI models with complete privacy across any cloud and on premises environments. With built-in autoscaling, robust governance, monitoring, and support for the best performing LLMs, it delivers reliable and scalable AI serving for enterprise workloads.
Deploy NVIDIA-optimized LLMs to achieve lower latency and higher throughput enabling more responsive applications and reduced TCO.
Cloudera AI deployment options
Deploy Cloudera AI anywhere with a cloud-native, portable, and consistent experience everywhere.
Cloudera on cloud
- Multi-cloud ready: Avoid lock-in and leverage AI Inference, agents, and AMPs with data from anywhere.
- Scalable: Scale compute resources dynamically, only paying for what you use.
- Full lifecycle integration: Seamlessly and securely share workloads and outputs across Cloudera experiences including Cloudera Data Engineering and Cloudera Data Warehouse.
Cloudera on premises
- Cost-effective: Optimize resource use for complex contextual modeling and AI workflows.
- Optimized performance: Meet SLAs with workload isolation and multi-tenancy.
- Collaborate effectively: Securely share workloads, data, models, and results across teams at every stage of the data lifecycle.
Customers
Delivering better, smarter banking experiences with data and AI

Take the next step
Explore the powerful capabilities of Cloudera AI in a hands-on experience or dive into the details in documentation.
Cloudera AI documentation
Dive into the details of how to get up and running with Cloudera AI, including step-by-step guidance on popular tasks.
Free Cloudera AI training
See how to quickly start projects using AMPs as well as a demo of how Cloudera AI supports all phases of the AI lifecycle.
Explore more products
Deploy and scale private AI applications, agents, and assistants with unmatched speed, security, and efficiency.
Unlock private generative AI and agentic workflows for any skill level, with low-code speed and full-code control.
Explore the end-to-end framework for building, deploying, and monitoring business-ready ML applications instantly.
Bring the power of AI to your business securely and at scale, ensuring every insight is traceable, explainable, and trusted.