Large Language Models (LLMs) will be at the core of many groundbreaking AI solutions for enterprise organizations. Here are just a few examples of the benefits of using LLMs in the enterprise for both internal and external use cases:
Optimize Costs. LLMs deployed as customer-facing chatbots can respond to frequently asked questions and simple queries. These enable customer service representatives to focus their time and attention on more high-value interactions, leading to a more cost-efficient service model.
Save Time. LLMs deployed as internal enterprise-specific agents can help employees find internal documentation, data, and other company information to help organizations easily extract and summarize important internal content.
Increase Productivity. LLMs deployed as code assistants accelerate developer efficiency within an organization, ensuring that code meets standards and coding best practices.
Several LLMs are publicly available through APIs from OpenAI, Anthropic, AWS, and others, which give developers instant access to industry-leading models that are capable of performing most generalized tasks. However, these LLM endpoints often can’t be used by enterprises for several reasons:
- Private Data Sources: Enterprises often need an LLM that knows where and how to access internal company data, and users often can’t share this data with an open LLM.
- Company-specific Formatting: LLMs are sometimes required to provide a very nuanced formatted response specific to an enterprise’s needs, or meet an organization’s coding standards.
- Hosting Costs: Even if an organization wants to host one of these large generic models in their own data centers, they are often limited to the compute resources available for hosting these models.
The Need for Fine Tuning
Fine tuning solves these issues. Fine tuning involves another round of training for a specific model to help guide the output of LLMs to meet specific standards of an organization. Given some example data, LLMs can quickly learn new content that wasn’t available during the initial training of the base model. The benefits of using fine-tuned models in an organization are numerous:
- Meet Coding Formats and Standards: Fine tuning an LLM ensures the model generates specific coding formats and standards, or provides specific actions that can be taken from customer input to an agent chatbot.
- Reduce Training Time: AI practitioners can train “adapters” for base models, which only train a specific subset of parameters within the LLM. These adapters can be swapped freely between one another on the same model, so a single model can perform different roles based on the adapters.
- Achieve Cost Benefits: Smaller models that are fine-tuned for a specific task or use case perform just as well as or better than a “generalized” larger LLM that is an order of magnitude more expensive to operate.
Although the benefits of fine tuning are substantial, the process of preparing, training, evaluating, and deploying fine-tuned LLMs is a lengthy LLMOps workflow that organizations handle differently. This leads to compatibility issues with no consistency in data and model organization.
Introducing Cloudera’s Fine Tuning Studio
To help remedy these issues, Cloudera introduces Fine Tuning Studio, a one-stop-shop studio application that covers the entire workflow and lifecycle of fine tuning, evaluating, and deploying fine-tuned LLMs in Cloudera’s AI Workbench. Now, developers, data scientists, solution engineers, and all AI practitioners working within Cloudera’s AI ecosystem can easily organize data, models, training jobs, and evaluations related to fine tuning LLMs.

Fine Tuning Studio Key Capabilities
Once the Fine Tuning Studio is deployed to any enterprise’s Cloudera’s AI Workbench, users gain instant access to powerful tools within Fine Tuning Studio to help organize data, test prompts, train adapters for LLMs, and evaluate the performance of these fine-tuning jobs:
- Track all your resources for fine tuning and evaluating LLMs. Fine Tuning Studio enables users to track the location of all datasets, models, and model adapters for training and evaluation. Datasets that are imported from both Hugging Face and from a Cloudera AI project directly (such as a custom CSV), as well as models imported from multiple sources such as Hugging Face and Cloudera’s Model Registry, are all synergistically organized and can be used throughout the tool – completely agnostic of their type or location.
- Build and test training and inference prompts. Fine Tuning Studio ships with powerful prompt templating features, so users can build and test the performance of different prompts to feed into different models and model adapters during training. Users can compare the performance of different prompts on different models.
- Train new adapters for an LLM. Fine Tuning Studio makes training new adapters for an LLM a breeze. Users can configure training jobs right within the UI, either leave training jobs with their sensible defaults or fully configure a training job down to custom parameters that can be sent to the training job itself. The training jobs use Cloudera’s Workbench compute resources, and users can track the performance of a training job within the UI. Furthermore, Fine Tuning Studio comes with deep MLFlow experiments integration, so every metric related to a fine tuning job can be viewed in Cloudera AI’s Experiments view.
- Evaluate the performance of trained LLMs. Fine Tuning Studio ships with several ways to test the performance of a trained model and compare the performance of models between one another, all within the UI. Fine Tuning Studio provides ways to quickly test the performance of a trained adapter with simple spot-checking, and also provides full MLFlow-based evaluations comparing the performance of different models to one another using industry-standard metrics. The evaluation tools built into the Fine Tuning Studio allow AI professionals to ensure the safety and performance of a model before it ever reaches production.
- Deploy trained LLMs to production environments. Fine Tuning Studio ships natively with deep integrations with Cloudera’s AI suite of tools to deploy, host, and monitor LLMs. Users can immediately export a fine-tuned model as a Cloudera Machine Learning Model endpoint, which can then be used in production-ready workflows. Users can also export fine tuned models into Cloudera’s new Model Registry, which can later be used to deploy to Cloudera AI’s new AI Inferencing service running within a Workspace.
- No-code, low-code, and all-code solutions. Fine Tuning Studio ships with a convenient Python client that makes calls to the Fine Tuning Studio’s core server. This means that data scientists can build and develop their own training scripts while still using Fine Tuning Studio’s compute and organizational capabilities. Anyone with any skill level can leverage the power of Fine Tuning Studio with or without code.
An End-to-End Example: Ticketing Support Agent
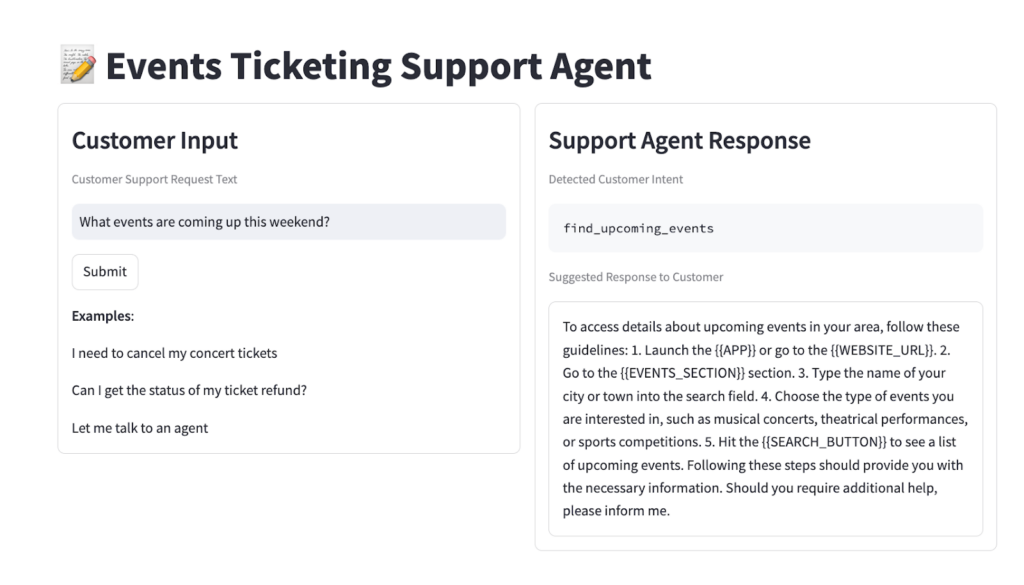
To show how easy it is for GenAI builders to build and deploy a production-ready application, let’s take a look at an end-to-end example: fine tuning an event ticketing customer support agent. The goal is to fine tune a small, cost-effective model that , based on customer input, can extract an appropriate “action” (think API call) that the downstream system should take for the customer. Given the cost constraints of hosting and infrastructure, the goal is to fine tune a model that is small enough to host on a consumer GPU and can provide the same accuracy as a larger model.
Data Preparation. For this example, we will use the bitext/Bitext-events-ticketing-llm-chatbot-training-dataset dataset available on HuggingFace, which contains pairs of customer input and desired intent/action output for a variety of customer inputs. We can import this dataset on the Import Datasets page.
Model Selection. To keep our inference footprint small, we will use the bigscience/bloom-1b1 model as our base model, which is also available on HuggingFace. We can import this model directly from the Import Base Models page. The goal is to train an adapter for this base model that gives it better predictive capabilities for our specific dataset.
Creating a Training Prompt. Next, we’ll create a prompt for both training and inference. We can utilize this prompt to give the model more context on possible selections. Let’s name our prompt better-ticketing and use our bitext dataset as the base dataset for the prompt. The Create Prompts page enables us to create a prompt “template” based on the features available in the dataset. We can then test the prompt against the dataset to make sure everything is working properly. Once everything looks good, we hit Create Prompt, which activates our prompt usage throughout the tool. Here’s our prompt template, which uses the instruction and intent fields from our dataset:


Train a New Adapter. With a dataset, model, and prompt selected, let’s train a new adapter for our bloom-1b1 model, which can more accurately handle customer requests. On the Train a New Adapter page, we can fill out all relevant fields, including the name of our new adapter, dataset to train on, and training prompt to use. For this example, we had two L40S GPUs available for training, so we chose the Multi Node training type. We trained on 2 epochs of the dataset and trained on 90% of the dataset, leaving 10% available for evaluation and testing.
Monitor the Training Job. On the Monitor Training Jobs page we can track the status of our training job, and also follow the deep link to the Cloudera Machine Learning Job directly to view log outputs. Two L40S GPUs and 2 epochs of our bitext dataset completed training in only 10 minutes.

Check Adapter Performance. Once the training job completes, it’s helpful to “spot check” the performance of the adapter to make sure that it was trained successfully. Fine Tuning Studio offers a Local Adapter Comparison page to quickly compare the performance of a prompt between a base model and a trained adapter. Let’s try a simple customer input, pulled directly from the bitext dataset: “i have to get a refund i need assistance”, where the corresponding desired output action is get_refund. Looking at the output of the base model compared to the trained adapter, it’s clear that training had a positive impact on our adapter!

Evaluate the Adapter. Now that we’ve performed a spot check to make sure training completed successfully, let’s take a deeper look into the performance of the adapter. We can evaluate the performance against the “test” portion of the dataset from the Run MLFlow Evaluation page. This provides a more in-depth evaluation of any selected models and adapters. For this example, we will compare the performance of 1) just the bigscience/bloom-1b1 base model, 2) the same base model with our newly trained better-ticketing adapter activated, and finally 3) a larger mistral-7b-instruct model.

As we can see, our rougueL metric (similar to an exact match but more complex) of the 1B model adapter is significantly higher than the same metric for an untrained 7B model. As simple as that, we trained an adapter for a small, cost-effective model that outperforms a significantly larger model. Even though the larger 7B model may perform better on generalized tasks, the non-fine-tuned 7B model has not been trained on the available “actions” that the model can take given a specific customer input, and therefore would not perform as well as our fine-tuned 1B model in a production environment.
Accelerating Fine Tuned LLMs to Production
As we saw, Fine Tuning Studio enables anyone of any skill level to train a model for any enterprise-specific use case. Now, customers can incorporate cost-effective, high-performance, fine-tuned LLMs into their production-ready AI workflows more easily than ever, and expose models to customers while ensuring safety and compliance. After training a model, users can use the Export Model feature to export trained adapters as a Cloudera Machine Learning model endpoint, which is a production-ready model hosting service available to Cloudera AI (formerly known as Cloudera Machine Learning) customers. Fine Tuning Studio ships with a powerful example application showing how easy it is to incorporate a model that was trained within Fine Tuning Studio into a full-fledged production AI application.
How can I Get Started with Fine Tuning Studio?
Cloudera’s Fine Tuning Studio is available to Cloudera AI customers as an Accelerator for Machine Learning Projects (AMP), right from Cloudera’s AMP catalog. Install and try Fine Tuning Studio following the instructions for deploying this AMP right from the workspace.
Want to see what’s under the hood? For advanced users, contributors, or other users who want to view or modify Fine Tuning Studio, the project is hosted on Cloudera’s github.
Get Started Today!
Cloudera is excited to be working on the forefront of training, evaluating, and deploying LLMs to customers in production-ready environments. Fine Tuning Studio is under continuous development and the team is eager to continue providing customers with a streamlined approach to fine tune any model, on any data, for any enterprise application. Get started today on your fine tuning needs, and Cloudera AI’s team is ready to assist in fulfilling your enterprise’s vision for AI-ready applications to become a reality.





